Programming Lang/Java
[이것이 자바다] Chapter 15. 컬렉션 자료구조
시데브
2025. 2. 2. 18:30
1. 컬렉션 프레임워크
- java.util 패키지에 널리 알려진 자료구조를 바탕으로 객체들을 효율적으로 추가, 삭제, 검색할 수 있도록 관련된 인터페이스와 클래스를 포함 -> Collection Framework
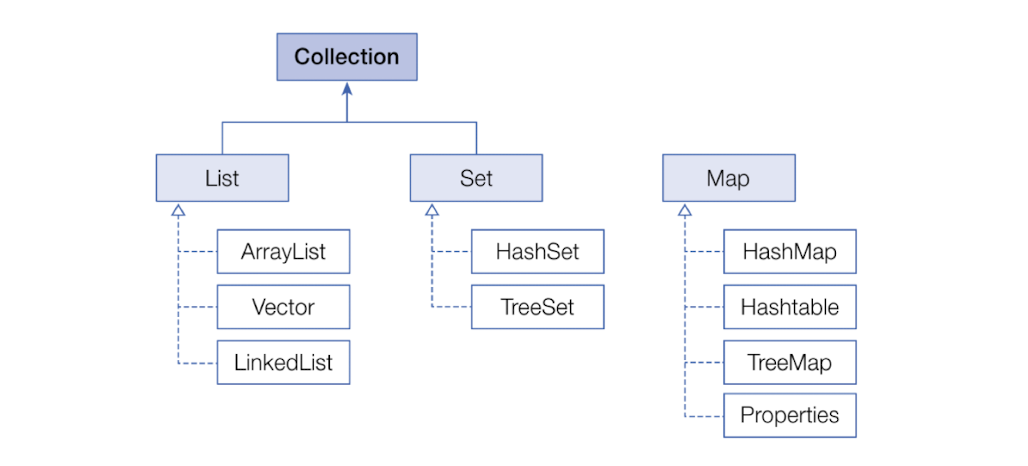
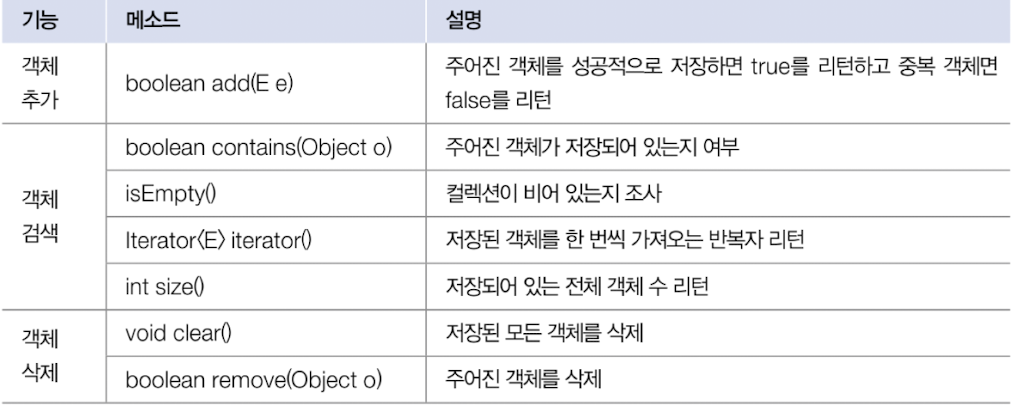
- List, Set: 객체를 추가, 삭제, 검색하는 방법에 있어서 공통점 존재 -> 공통된 methods를 따로 모아 Collection interface로 정의
- Map: key와 value를 하나의 쌍으로 묶어서 관리하는 구조

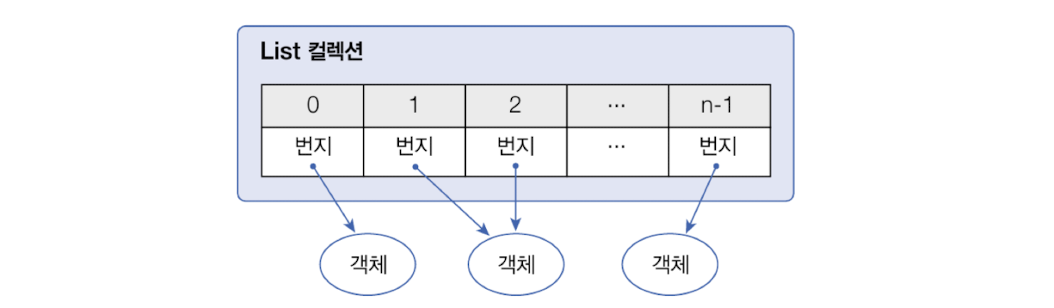
2. List 컬렉션

2.1. ArrayList
- ArrayList에 객체를 추가하면 내부 배열에 객체가 저장
- 일반 배열과의 차이점은 제한 없이 객체를 추가할 수 있다는 점
- 객체의 번지를 저장
- 동일한 객체 중복 저장 가능 -> 동일한 번지 저장
- null 저장 가능
List<E> list = new ArrayList<E>(); // E에 지정된 타입의 객체만 저장
List<E> list = new ArrayList<>(); // E에 지정된 타입의 객체만 저장
List list = new ArrayList(); // 모든 타입의 객체를 저장- 객체 추가, 제거 과정에서 뒤 인덱스에 위치한 요소들이 모두 당겨지거나 밀려남 -> 빈번한 객체 삽입, 삭제에 불리
2.2. Vector
- Vector는 ArrayList와 동일한 내부 구조를 가짐
- synchronized methods로 구성되어, multiple threads가 동시에 Vector() method 실행 불가
- multiple threads 환경에서 안전하게 객체를 추가 또는 삭제 가능
List<E> list = new Vector<E>(); // E에 지정된 타입의 객체만 저장
List<E> list = new Vector<>(); // E에 지정된 타입의 객체만 저장
List list = new Vector(); // 모든 타입의 객체를 저장2.3. LinkedList
List<E> list = new LinkedList<E>(); // E에 지정된 타입의 객체만 저장
List<E> list = new LinkedList<>(); // E에 지정된 타입의 객체만 저장
List list = new LinkedList(); // 모든 타입의 객체를 저장- 삽입, 삭제 연산의 시간적 측면 ArrayList보다 유리
3. Set 컬렉션
- 저장 순서 유지 X
- 객체 중복 저장 불가능
- 하나의 null만 저장 가능
3.1. HashSet
Set<E> set = new HashSet<E>();
Set<E> set = new HashSet<>();
Set set = new HashSet();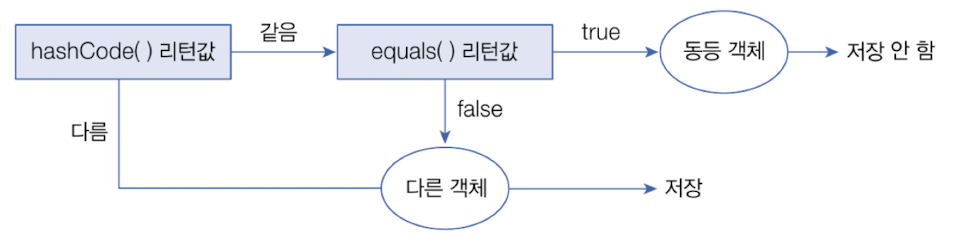
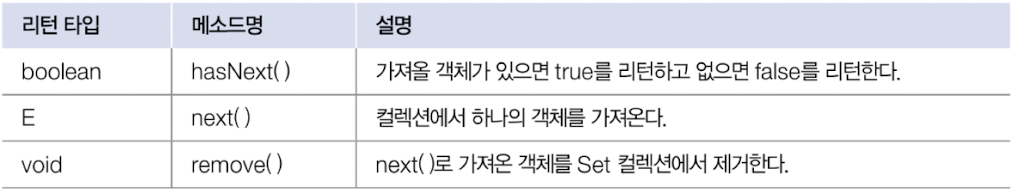
- Set collection은 index로 객체를 탐색하는 method가 없음 -> 객체를 한 개씩 반복해서 탐색
- for문 이용
- iterator() method로 iterator를 얻어, 하나씩 가져오는 방법
Set<E> set = new HashSet<>();
// for문
for(E e : set) {
...
}
// iterator
Iterator<E> iterator = set.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
E e = iterator.next();
}
4. Map 컬렉션
- Map collection: key와 value로 구성된 entry 객체를 저장
- key는 중복 저장 X
- value는 중복 저장 O

4.1. HashMap

-> key에 대해서 중복 여부 확인
Map<K, V> map = new HashMap<K, V>();4.2. Hashtable
- Hashtable은 HashMap과 동일한 내부 구조를 가짐
- synchronized methods로 구성되어, multiple threads가 동시에 hashtable methods를 실행 불가능
- 멀티 스레드 환겨에서 안전하게 객체를 추가, 삭제
Map<String, Integer> map = new Hashtable<String, Integer>();
Map<String, Integer> map = new Hashtable<>();
4.3. Properties
- Properties는 Hashtable의 자식 클래스
- Properties: key&value를 string type으로 제한한 collection
- 주로 확장자가 .properties인 프로퍼티 파일을 읽을 때 사용
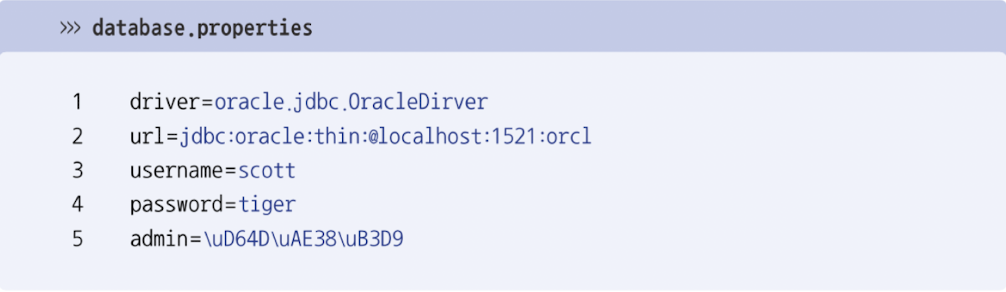
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(Xxx.class.getResourceAsStream("database.properties"));- getResourceAsStream(): 주어진 상대 경로의 resource file을 읽는 InputStream을 리턴
5. 검색 기능을 강화시킨 컬렉션
5.1. TreeSet
- TreeSet: binary tree를 기반으로 한 Set Collection
- 부모 노드의 객체보다 낮은 것은 왼쪽 자식 노드, 높은 것은 오른쪽 자신 노드에 저장
TreeSet<E> treeSet = new TreeSet<E>();
TreeSet<E> treeSet = new TreeSet<>();

5.2. TreeMap
- TreeMap: binary tree를 기반으로 한 Map Collection
- 키와 값이 저장된 Entry를 저장한다는 점에서 TreeSet과 차이 존재
- key 값을 기준으로 정렬

TreeMap<K, V> treeMap = new TreeMap<K, V>();
TreeMap<K, V> treeMap = new TreeMap<>();
5.3. Comparable과 Comparator
- TreeSet, TreeMap에 저장되는 객체(키 객체)는 저장과 동시에 오름차순으로 정렬 -> Comparable interface를 구현하고 있어야 가능
- Integer, Double, String type은 모두 Comparable을 구현한 상태
- 사용자 정의 객체를 저장할 때에는 반드시 Comparable을 구현해야 함
- Comparable interfae에는 compareTo() method 정의됨 -> 사용자 정의 클래스에서 이 메소드를 재정의해서 비교 결과를 정수 값으로 리턴해야 함
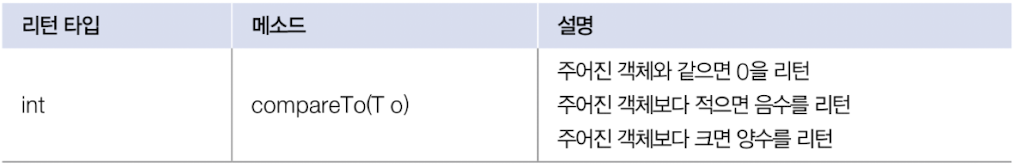
- 비교 기능이 있는 Comparable 구현 객체를 TreeSet에 저장하나, TreeMap의 키로 저장하는 것이 원칙이나, 비교 기능이 없는 Comparable 비구현 객체를 저장하고 싶다면 TreeSet과 TreeMap을 생성할 때 비교자(Comparator)를 제공
- 비교자는 Comparator interface를 구현한 객체를 의미
- Comparator interface에는 compare() method가 정의되어 있음
TreeSet<E> treeSet = new TreeSet<E>( new ComparatorImpl() );
TreeMap<K, V> treeMap = new TreeMap<K, V>( new ComparatorImpl() );
6. LIFO와 FIFO 컬렉션
6.1. Stack
Stack<E> stack = new Stack<E>();
Stack<E> stack = new Stack<>();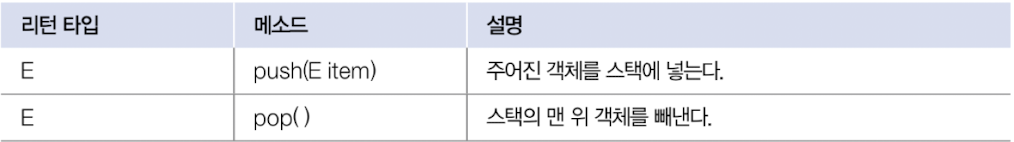
6.2. Queue
Queue<E> queue = new LinkedList<E>();
Queue<E> queue = new LinkedList<>();
7. 동기화된 컬렉션
- collection framework의 대부분의 클래스들은 single thread 환경에서 사용할 수 있도록 설계됨 - vector, hashtable 제외
- ArrayList, HashSet, HashMap을 멀티 스레드 환경에서 사용하기 위해서, collection framework는 asynchronized method를 synchronized method로 래핑하는 synchronizedXXX() method 제공

8. 수정할 수 없는 컬렉션
- unmodifiable collection: 요소를 추가, 삭제할 수 없는 컬렉션
- 컬렉션 생성 시, 저장된 요소를 변경하고 싶지 않을 때 유용
- 생성 방법
- List, Set, Map interface의 static method인 of()
- List, Set, Map interface의 static method인 copyOf() -> 기존 컬렉션을 복사하여 수정할 수 없는 컬렉션 생성
- 배열로부터 수정할 수 없는 List collection 생성
// of()
List<E> immutableList = List.of(E... elements);
Set<E> immutableSet = Set.of(E... elements);
Map<K, V> immutableMap = Map.of( K k1, V v1, K k2, V v2, ... );
// copyOf()
List<E> immutableList = List.copyOf(Collection<E> coll);
Set<E> immutableSet = Set.copyOf(Collection<E> coll);
Map<K, V> immutableMap = Map.copyOf(Map<K, V> map);
// 배열로부터 수정 불가능한 List collection 생성
String[] arr = { "A", "B", "C" };
List<String> immutableList = Arrays.asList(arr);참고자료
728x90
반응형