| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
Tags
- 머신러닝
- Machine Learning
- 회귀
- LG
- Classification
- 지도학습
- LG Aimers 4th
- supervised learning
- 오블완
- AI
- LG Aimers
- 해커톤
- 딥러닝
- deep learning
- gpt
- regression
- LLM
- GPT-4
- PCA
- ChatGPT
- 티스토리챌린지
- OpenAI
- 분류
Archives
- Today
- Total
SYDev
[컴퓨터 구조] 1, 2주차 정리 본문
경희대학교 컴퓨터공학부 김정욱 교수님의 컴퓨터 구조 강의 내용을 기반으로 한 정리
Class of Computing Applications
PC(Personal Computer)
- 다목적 microcomputer(마이크로 프로세서를 cpu로 사용하는 컴퓨터)
- 크기, 용량, 가격 면에서 개인적으로 사용하기에 적합
- PC는 보통 다음 part들을 포함
- computer case
- power supply
- motherboard(메인보드)
- random access memory(RAM) -> contemporary data(power off -> gone)
- Hard disk -> real data(power off -> save)
- External devices(e.g., visual display, keyboard, printer, etc.)
Server
- multi user computer
- 동시에 multiple users가 사용할 수 있는 larger programs를 돌리기 위해 사용
- 네트워크를 통해 접근
- pc와 같은 기술구조, but larger computing, storage, input/output capacity
Supercomputer
- Extreme case of the server
- 큰 규모의 processors & memory & costs
Embedded computer
- 다른 기기 안에 있는 컴퓨터 -> 미리 제작된 application(응용 프로그램)
- hardware 안에 미리 내장되기에, 한 번 import하면 변경이 어려움
PMD(Personal Mobile Device)
- no keyboard and mouse
- touch-sensitive screen
Cloud computing
- store, manage and access data online
- lower cost
server -> 내부망도 포함하는 개념
cloud -> 내부망으로만 접근 불가능
Hard Disk Storage 용량의 차이?
용량이 표기 상으로 1TB 인 하드 디스크가 있다면 제조사에서는 편리를 위해 1TB = 1,000GB = 1,000,000MB = 1,000,000,000KB = 1,000,000,000,000Byte 를 저장할 수 있다고 표시합니다 . 그런데 , 윈도우에서는 1024 로 나누어 1,000,000,000,000Byte = 976,562,500KB = 953,674MB = 931GB (= 0.909TB) 가 되어서 , 최종적으로 931GB 로 표시됩니다 .
(출처: https://cs-apj-static.ext.hp.com/css-apj-km/KR/doc/5c1f90eca3fcabd69627d0c00e5ba83e/googleContent.html)
-> 표기상으로는 편리하게 1000으로 나누지만 실상은 1024로 나눔
Eight Great Ideas in Computer Architecture
- 무어의 법칙, 2-3년마다 IC 개수가 약 2배씩 늘어남 -> 요즘 틀리기 시작함
- 디자인을 간단하게 보기 위해 -> 추상화
- common case fase -> cache memory, 자주 쓸 것들은 make faster
- parallelism
- pipelining
- prediction -> 다음에 뭐 쓸지 예상, 미리 준비
- Hierarchy of memories -> 메모리의 계층적 구조, cache memory <-> disc
- redundancy-> 중복되는 값들 여러 개 놓고, 맞는 것들을 이용 -> 신뢰성 향상
Below Our Programs
Applications software
- 특정 기능을 수행하는
- 프로그램, 워드, 메일, 문서, 유튜브
systems software
- 컴퓨터 시스템 운영에 필요한 프로그램
- Operating system -> hardware wroks를 control하는 sw
- windows, macOS, Linux, etc.
Compiler
- high-level language 번역
- C, Java 등의 언어 번역
Hardware
- 보조기억장치, 출력장치, 주기억장치, 입력장치, 중앙처리장치
High-level programe languages
Assembly languages
Binary machine languages
- 이진법 표현
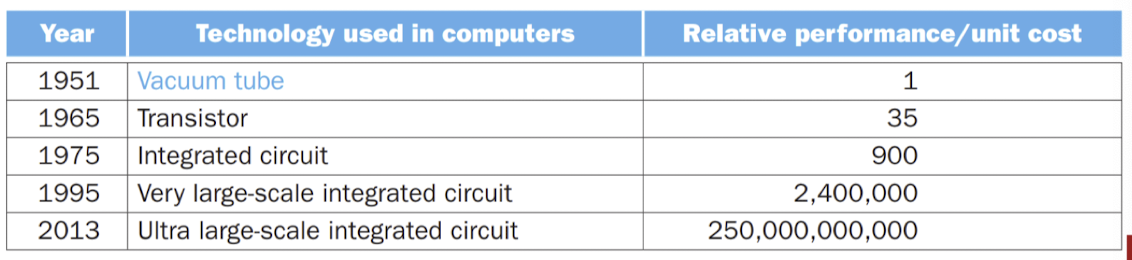
Performance Growth per Unit Cost
- Integrated ciurcuit -> 수백개의 트랜지스터가 하나의 chip에 존재
- VLSI(Very Large-Scale Intergrated circuit)
Performance Growth in DRAM
- DRAM: 저장된 데이터가 시간과 전원의 끊김에 따라 소멸되는 RAM

Measuring Performance
Measurement of Performance
- Clock speed
- CPI(Clock Cycles per Instruction)
- MIPS(Millions of Instructions per Second)
- Etc.
Performance
Defining performance
- 상황에 따라 성능이 다르게 평가될 수 있다.

-> passenger capacity, cruising speed, 기준을 바꾸면 성능 지표도 달라진다.
Time
- response time(execution time): Second(s)/Program

CPU execution time
- CPU Clock cycles와 Clock cycle time과 관계있다.
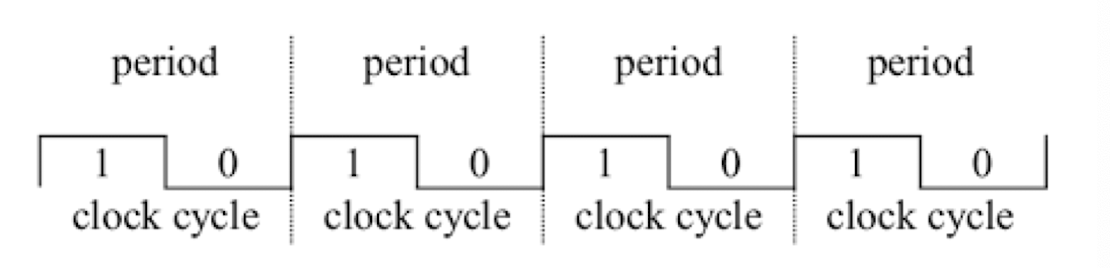
- CPU execution time = CPU clock cycles for a program * Clock cycle time = CPU clock cycles for a program / Clock rate
- Clock cycles Per Instruction (CPI) -> 각 명령이 수행되기 위해 필요한 clock cycle 개수
- CPU clock cycles = Instructions for a program X Average clock cycles per instruction

CPU performance equation
CPU time = Instruction count * CPI * Clock cycle time = Instruction count * CPI / Clock rate


Understanding Program Performance
Algorithm(Instruction count, CPI)
- 프로그램의 instructions & 프로세서의 instructions를 결정
- slower or faster instructions -> CPI에도 영향
Programming Language
- instruction count에 영향을 준다 -> language가 processor instructions로 변환되기 때문
- CPI에도 영향을 줌
Compiler
- source language instructions를 computer instructions로 변환하는 과정을 결정함
Instructions Set Architerture (ISA)
- 명령어 집합 구조 -> 덧셈, 곱셈과 같은 약속들을 CPU에서 정해둔 것
- 함수마다 필요한 명령어 수가 다르고, 각 명령어마다 필요한 cycles 또한 다름, processor의 전체 clock rate도 다름
The Power Wall
- Clock rate & Power는 서로 연관됨, 10년동안 가파르게 성능이 오르다가, 최근에 완만해짐
MIPS(Million Instructions Per Second)
- 백만개의 명령어를 가진 프로그램의 실행시간 -> 측정

Three issues of using MIPS
- MIPS는 실행속도를 의미하지, 명령어 하나가 얼마나 많은 일을 수행하는지 알 수 없다.
- 같은 컴퓨터에서도 어떤 프로그램을 실행하느냐에 따라 MIPS 값을 다르다
- 새 프로그램이 더 많은 수의 명령어를 실행하지만 각각의 명령어 속도가 빠르다면 -> MIPS는 performance와는 독립적으로 다양해질 수 있다.
Summary
Execution time -> 얼마나 명령어를 적게 사용하느냐, 얼마나 clock cycle이 적은 명령어를 사용하느냐, 얼마나 cpu가 좋으냐
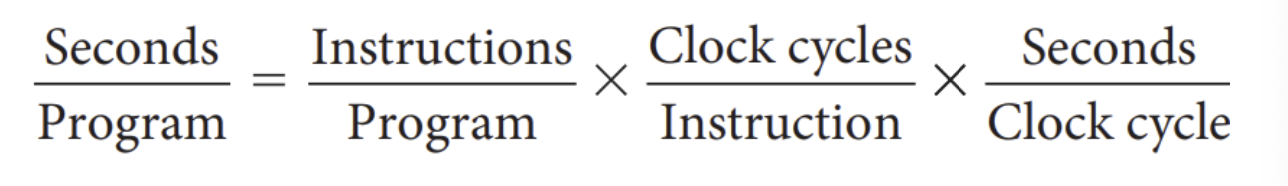
728x90
반응형
'3학년 1학기 전공 > 컴퓨터 구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [컴퓨터 구조] Lecture 09: Arithmetic for Computers (0) | 2024.04.13 |
|---|---|
| [컴퓨터 구조] Lecture 08: Instructions - Language of the Computer (0) | 2024.04.13 |
| [컴퓨터 구조] Lecture 07: Instructions - Language of the Computer (0) | 2024.04.05 |
| [컴퓨터 구조] Lecture 06: Instructions - Language of the Computer (1) | 2024.04.04 |
| [컴퓨터 구조] 3주차 정리 (1) | 2024.03.22 |




