| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 |
| 30 |
- gpt
- LG Aimers 4th
- regression
- LG
- LG Aimers
- 분류
- 티스토리챌린지
- 지도학습
- 해커톤
- ChatGPT
- supervised learning
- 오블완
- PCA
- 머신러닝
- GPT-4
- LLM
- AI
- Machine Learning
- Classification
- 딥러닝
- OpenAI
- 회귀
- deep learning
- Today
- Total
SYDev
[마이크로서비스프로그래밍] Lecture04 - Virtualization & Container Technology 본문
[마이크로서비스프로그래밍] Lecture04 - Virtualization & Container Technology
시데브 2024. 9. 13. 19:15경희대학교 이성원 교수님의 마이크로서비스 프로그래밍 수업을 기반으로 정리한 글입니다.
Learning Objective
- virtualization & container technology의 핵심 개념
Virtualization
- computer science에서의 Virtualization -> 무언가의 virtual version을 만드는 행위
- Virtual computer, hardware platforms, storage divices, computer network resources

-> virtual machine - sofrware 기반으로 구현된 것
1. Types of Virtualization
- Software
- Memory
- Storage
- Data
- Network
2. Role of Virtualization
- 하나의 컴퓨터 위에서 multiple OS instances를 동시에 실행 가능하도록 하는 역할
- Host OS에서 hardware를 분리하는역할

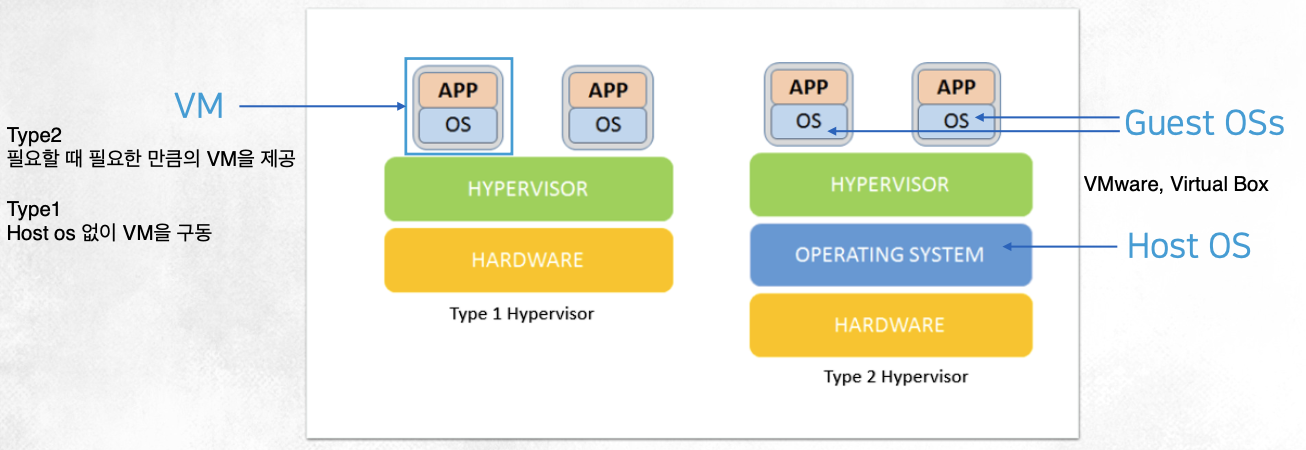
3. Hypervisor
- Hypervisor Virtualization
- Hypervisor: Host OS(Type 2. Hosted) or Hardware(Type 1. Bare Metal) 위에 추가되는 new layer
- Hypervisor는 host machine 위에서 multiple VM machines를 실행할 수 있음
- 각 VM은 서로 다른 Guest OS 세트를 실행할 수 있음 -> Guest OS는 application을 실행
- Hypervisor Software
- Hypervisor Software -> virtual machine monitor
- Hypervisor Software: virtual machines를 생성하고 실행하는 process
- 하나의 host computer가 multiple guest VMs를 실행할 수 있게 해줌 -> memory & processing 같은 자원을 가상으로 공유
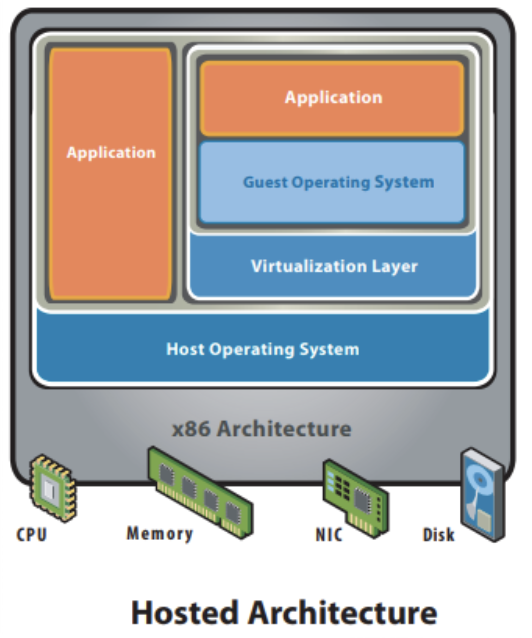
- Hosted Hypervisor Architecture
- Host OS 위에서 동작 -> device support & physical resource management
- Benefits of Using Hypervisors
- Cost Efficient -> 각각의 physical machine은 multiple VMs로 나눠짐 -> cost effective
- Easy to scale
- cloud environment에 배포된 VM's는 scale 조절이 쉽다 -> 필요한 개수 만큼 만들어낼 수 있다.
- physical machines를 주문하거나 구성할 필요가 없음 -> 간단하게 VM 추가 가능
4. Problems of Virtual Machine
- 각 VM은 os, application, binaries and libraries의 full copy를 포함 -> 수십 GBs
- slow to boot
- "(Guest) Linux over (Host) Linux" problem -> data center의 Host os와 user가 필요로 하는 Guest os가 중복되는 문제
- 굳이 linux os 위에 linux os를 더 올릴 필요가 없음 -> 비효율적

- Computer를 빌려서 사용하는 것이 목적 X -> multiple applications를 실행하는 것이 본래 목적
- N개의 computers -> N개의 applications에 집중
- 기존에 여러 개이 application을 동시에 실행하는 개념 -> Unix: multi-user 방식으로, user를 삭제하면 설치하기 이전 상태로 깔끔하게 복구 -> 여기서 더 발전시킨 것이 Container Linux -> 그러나 Linux에만 적용됨
- application 하나를 실행할 때, 필요한 모든 것을 container에 담았다가, 다 쓰면 삭제
- Docker -> window, unix, ... 다양한 os에 적용 가능
Container
1. Container vs Virtual Machine

-> Virtual machine 방식은 Guest os가 Host os와 같은 상황이 발생하면 비효율적
-> Containerized Applications - 각 application은 VM과 유사하게 스스로의 rousources(disk, network, ..)를 가진 것처럼 인식됨 -> but, VM 만큼 무겁진 않음
- Execution Time

- Memory Usage

-> docker가 vm에 비해 상대적으로 매우 적은 memory 사용량을 가짐
- CPU Utilization
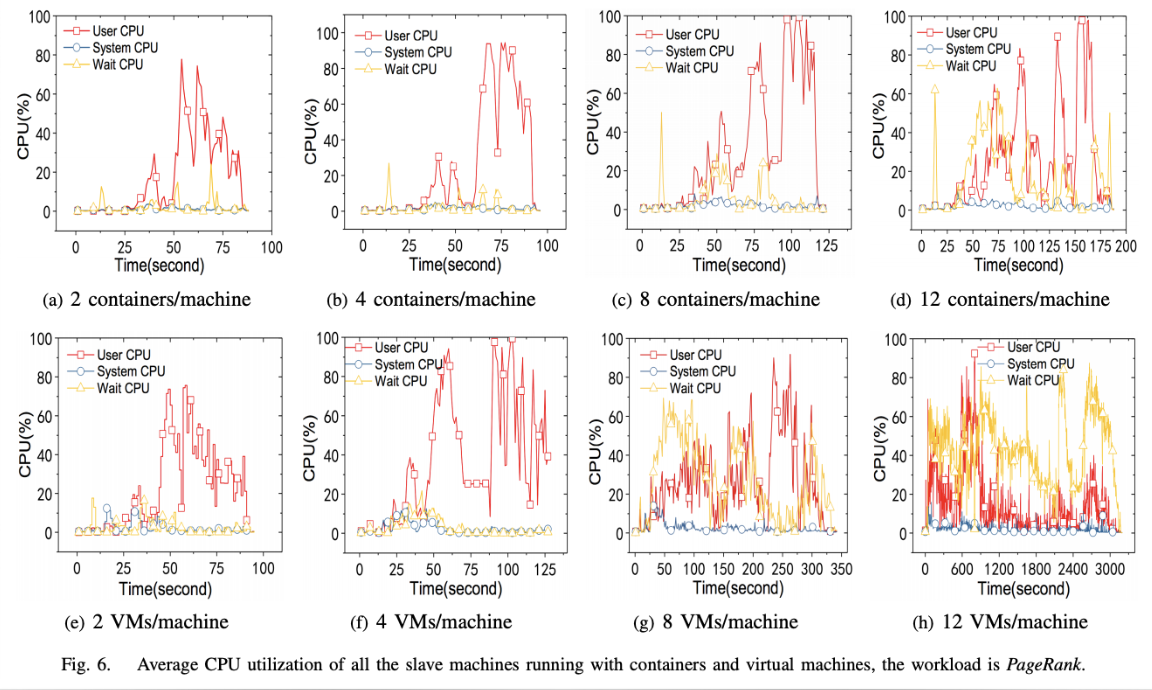
-> 키고 끄는 것이 빠르다.
2. Container
- 필요한 프로그램을 설치하고, 나중에 깨끗하게 지울 수 있음
- Container: code와 dependencies를 패키지화한 app layer의 추상적 개념
- Multiple Containers는 같은 machine에서 동작
- OS kernel을 other containers와 공유 -> server 환경에서 생성되기 때문에, user space에서 다른 container와 분리된 processes
- 같은 os를 공유하지만, 서로 다른 memory, disk, network를 가짐
- VM 보다 작은 공간을 차지함 -> typically 수십 MBs (images)
- 더 적은 VMs와 OS를 요구 -> 더 많은 applications를 다룰 수 있음
- operating system level에서 가상화됨
- Containers are far more lightweight
- 같은 OS kernel을 공유
- 시작이 더 빠름
- 전체 OS를 부팅하는 것보다 메모리 사용량이 적음
3. Challenges of Container
- Staff education
- Re-architecting applications
- Platform issues
'3학년 2학기 전공 > 마이크로서비스프로그래밍' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [마이크로서비스프로그래밍] Lecture06 - Docker Overview (2) | 2024.09.17 |
|---|---|
| [마이크로서비스프로그래밍] Lecture05 - Docker Introduction (1) | 2024.09.17 |
| [마이크로서비스프로그래밍] Lecture03 - Infrastructure & Virtualization (8) | 2024.09.13 |
| [마이크로서비스프로그래밍] Lecture02 - Cloud Computing & Infrastructure (7) | 2024.09.12 |
| [마이크로서비스프로그래밍] Lecture01 - Overview (13) | 2024.09.11 |




