| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 | 31 |
Tags
- supervised learning
- gpt
- LG Aimers 4th
- deep learning
- 해커톤
- 티스토리챌린지
- Classification
- 회귀
- LG Aimers
- regression
- 지도학습
- Machine Learning
- PCA
- ChatGPT
- OpenAI
- 오블완
- GPT-4
- LLM
- AI
- 머신러닝
- 딥러닝
- 분류
- LG
Archives
- Today
- Total
SYDev
[컴파일러] Chapter 5. Semantic Analysis 본문
경희대학교 허선영 교수님의 컴파일러 수업을 기반으로 정리한 글입니다.
0. Introduction
- Understanding the meaning of a sentence -> 문장의 의미를 유추
- Check ambiguity & type
- ex) Jack and Jack left her homework at home
- 잭은 몇 명?
- jack과 her의 미스매치
1. Semantic Analysis
- each expression이 correct type을 가지는지
- x + y -> x는 int, y는 string이면 error
- translate Abstract Syntax Tree -> Intermediate Representation(IR) Trees

- Semantic analyzer also can check
- All identifiers(Variable, Class, Functions, Methods, ...) -> 한 번만 선언됐는지
- parser에서도 가능 -> compiler designer들이 결정
- Inheritance Relationship - 상하관계
- Types are well defined and related
- Reserved Identifiers가 잘못 사용되지는 않았는지
- All identifiers(Variable, Class, Functions, Methods, ...) -> 한 번만 선언됐는지
- Motivation
- Lexical Analysis: 잘못된 Tokens를 Detecting
- ex) 123foo -> 처리할 수 없는 토큰
- Parsing: 문법을 잘못 작성한 경우
- ex) if then 절에 if(조건문) -> 조건문 부분을 뺀 경우
- Semantic Analysis
- ex) abc + 3 -> parser cannot catch the error
2. Symbol Table
- Symbol Table(Environment)
- main data structure in semantic analysis
- Identifiers(variables, functions, class name, ..)-> types & loactions 매핑
- identifier가 어떤 type에 mapping됐는지를 저장 -> bindings라 부름
- ex){g ↦ string, a ↦ int}
- exmaple
- 𝜎0: Initial environment

-> 가장 가까운 binding 사용
-> 범위를 벗어나면 이전 정의로 회귀
2.1. Symbol Table - Implementation
- Imperative Style
- single global environment
- beginning-of-scope 진입
- table에 entries 추가
- end-of-scope 도달
- previous addition을 제거
- Functional Style
- beginning-of-scope 진입
- old one에 추가함으로써, 새로운 environment 생성
- old table remains pristine
- end-of-scope 도달
- retrieve old table
- beginning-of-scope 진입
2.3. Imperative Symbol Table
- Symbol tables must permit efficient lookup of identifiers -> id의 type을 빠르게 찾아낼 수 있어야 함
- Hash Tables - an array of buckets
- Bucket - linked list of entires(각 entry에 binding 하나 존재)

- simplest example) string length를 bucket id로 사용 -> length에 대한 modulo 연산을 id로 사용
- Symbol table을 하나만 유지!!
- Insert new element at front of bucket
- example) val a: string = "x" -> h(a) = 0
- Remove each symbol at the end of the scope
- example) pop(a)
- Insert new element at front of bucket
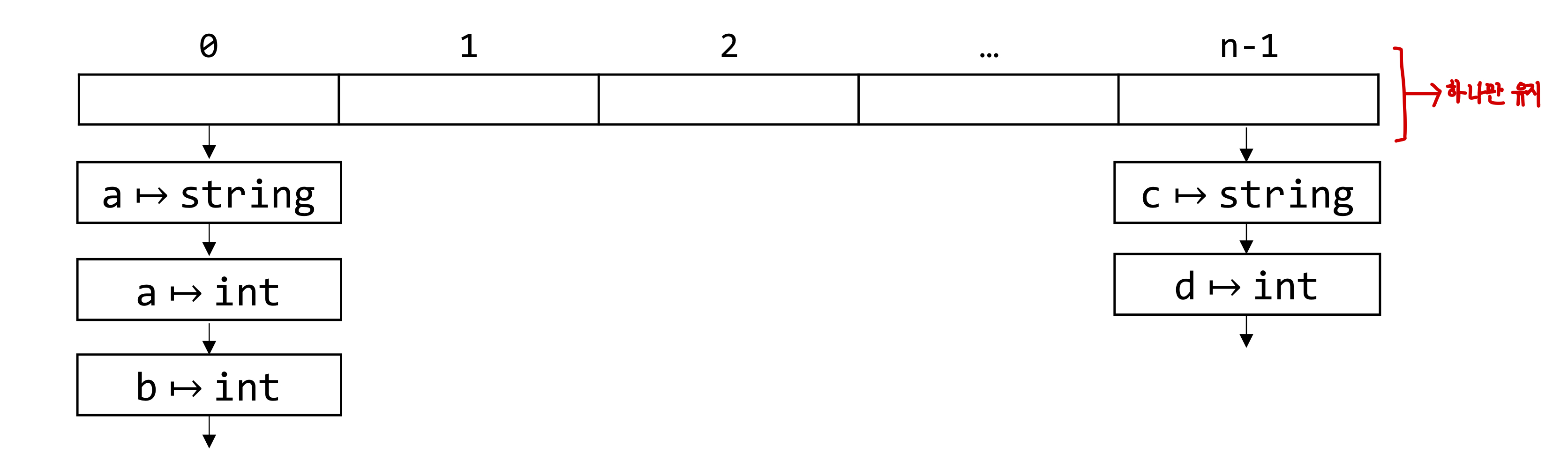
2.4. Functional Symbol Table
- 기존 테이블을 수정하는 방식 X -> new table을 생성
- example) val a: string = "x"
- 기존 테이블을 link하는 식으로 효율적으로 테이블 생성
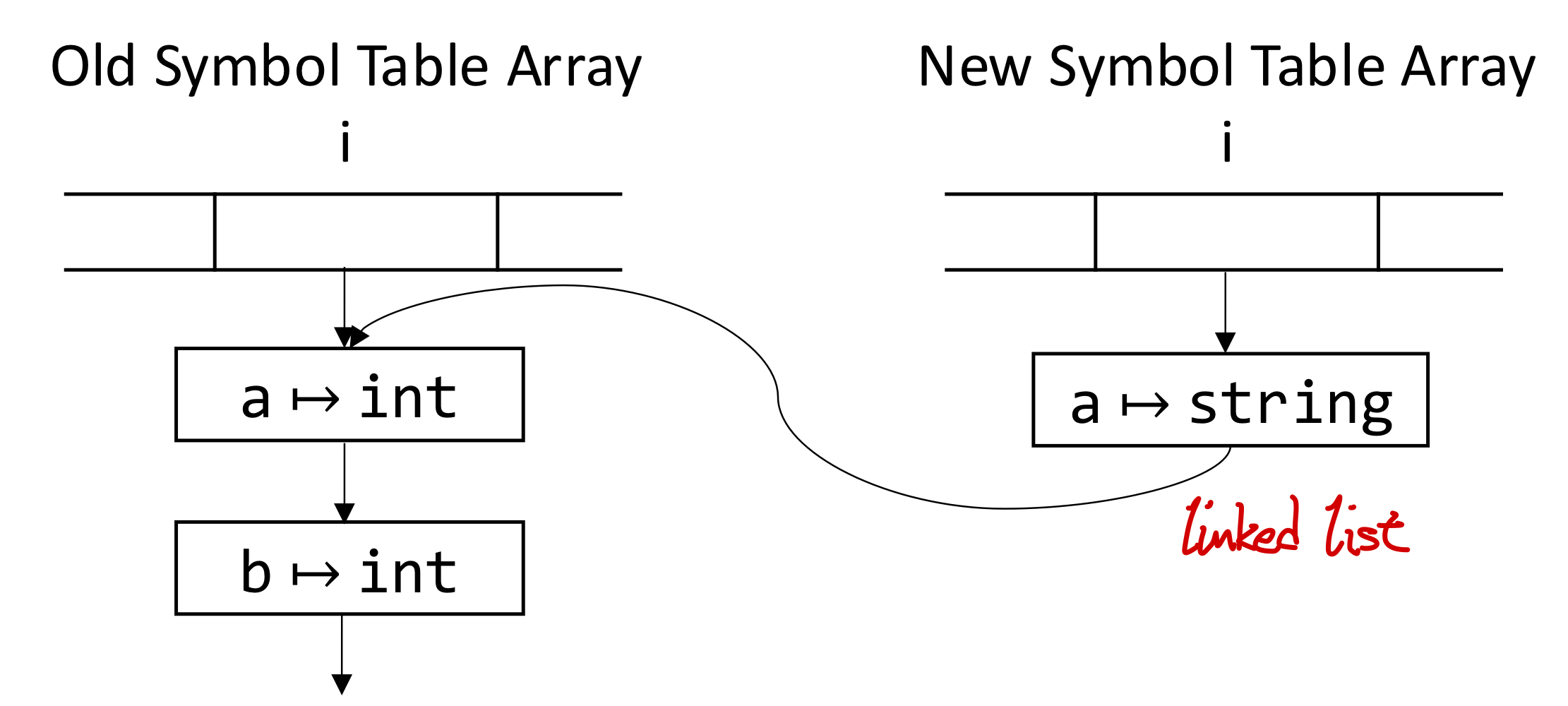
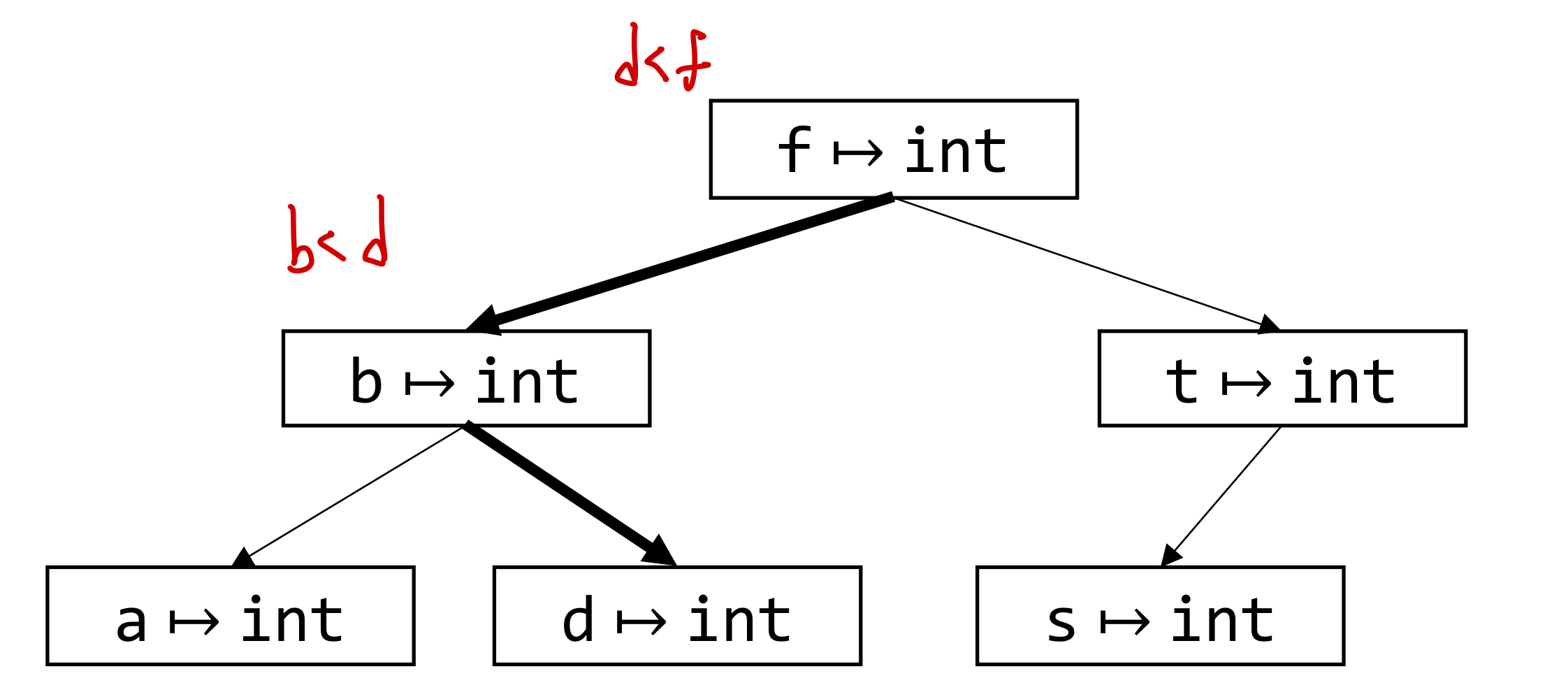
- Better Medhot: use binary search trees
- BST
- easy insertion
- tree build 시에 ordering이 필요할 시에


3. Type System
- Type System
- typing rules의 집합으로 구성
- typing rules -> expressions에 types 할당
- 어떤 type에 어떤 operations가 valid한지 특정
- typing rules의 집합으로 구성
- Type Checking
- expression의 type이 type system에 따라 유효한지 검사
- operations가 올바른 type과 사용되었는지 보장
- Type Inference(타입 추론)
- type system에 따라, type을 자동으로 추론
- 생략된 타입 정보를 자동으로 채움
- ex) let = 3일 때, x의 타입은 자동으로 int로 추론
3.1. Typing Rule
- expression에 type을 할당하기 위한 유도 법칙
- if hypothesis(가정) is true -> conclusion is true
- ex) if e1 has type t1 & e2 has type t2 -> e3 has type T3
- A typing rule: 𝑒1: 𝑇 1 ∧ ⋯ ∧ 𝑒𝑛: 𝑇 𝑛 ⇒ 𝑒: 𝑇
- Hypothesis ⇒ Conclusion
- if hypothesis is true, then conclusion is true
- e: T
- e has type T
- Symbol ∧
- and
- Hypothesis ⇒ Conclusion
- example
- (𝑒1: 𝐼𝑛𝑡 ∧ 𝑒2: 𝐼𝑛𝑡) ⇒ 𝑒1 + 𝑒2: 𝐼𝑛𝑡
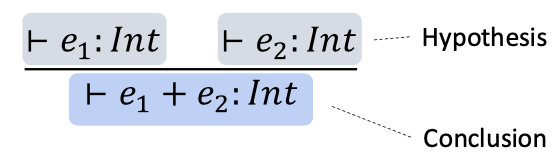
- axiom: inference rule with no premise(가정) -> always true


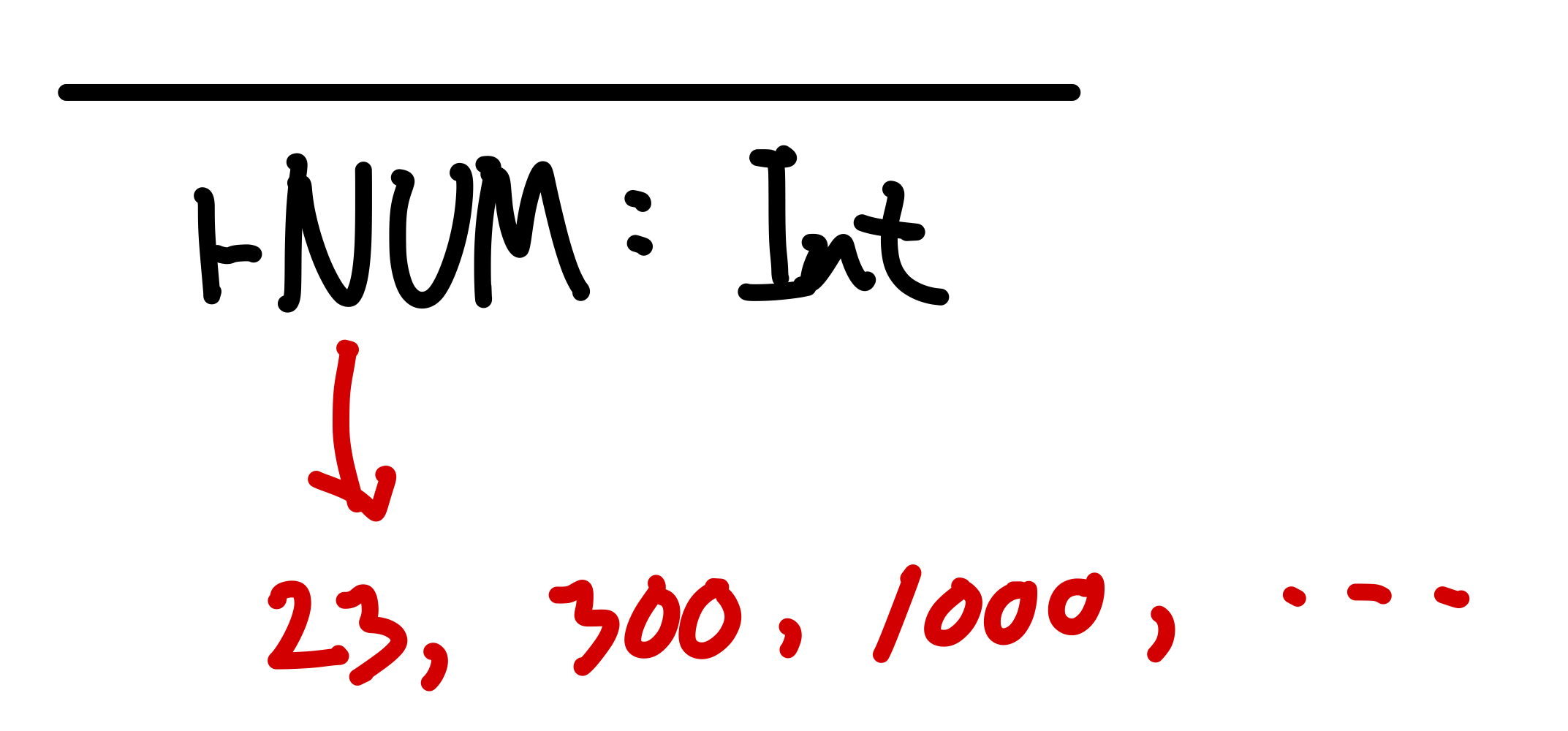
3.2. Type Inference
- expression의 type을 유도하기 위해 -> type system의 typing rules 사용
- Build a Derivation tree(Typing Derivation) by applying typing rules
- example
- Grammar
- E -> NUM
- E -> E + E
- Type System

- Type Inference: 1 + 2
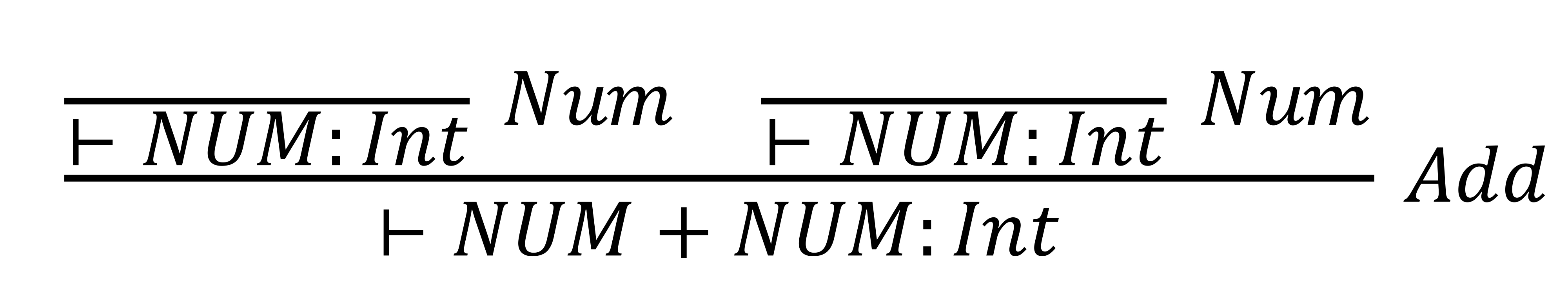
-> 완성된 derivation tree
-> axiom으로부터 하나씩 type 추론
3.3. Type Environment
- Problem: What is the type of a variable?

- Solution
- Put more informaiton in the rules
- Type environment gives the types of variables

- Γ ⊢ 𝑒 ∶ 𝐴 ⇔ expression e has type A under type environment Γ
- example






- What is type of the following expression?


- Fun & Arg
- Type System

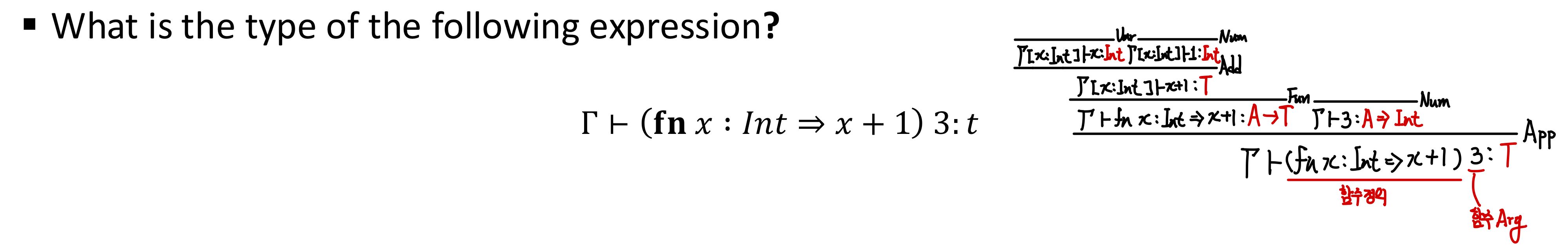
4. Subtyping
- Subtyping: Compatibility(호환성) of interfaces
- A에 대한 subtype B -> A 객체에서 호출 가능한 모든 함수: B 객체에서도 호출 가능
- A를 호출하는 function에 B가 대신 들어갈 수 있는가!!
- Inheritance: Reuse of implementations
- A를 상속하는 B -> A의 구현을 재사용할 수 있다는 뜻

-> input 1개로 f를 호출 가능하지만, g는 호출 불가능: g는 f의 subtype X
-> input 2개로 g를 호출 가능, 또한 f도 호출 가능: f는 g의 subtype 가능
4.1. Subtyping Rules
- Reflectivity: 스스로의 subtype이 될 수 있음
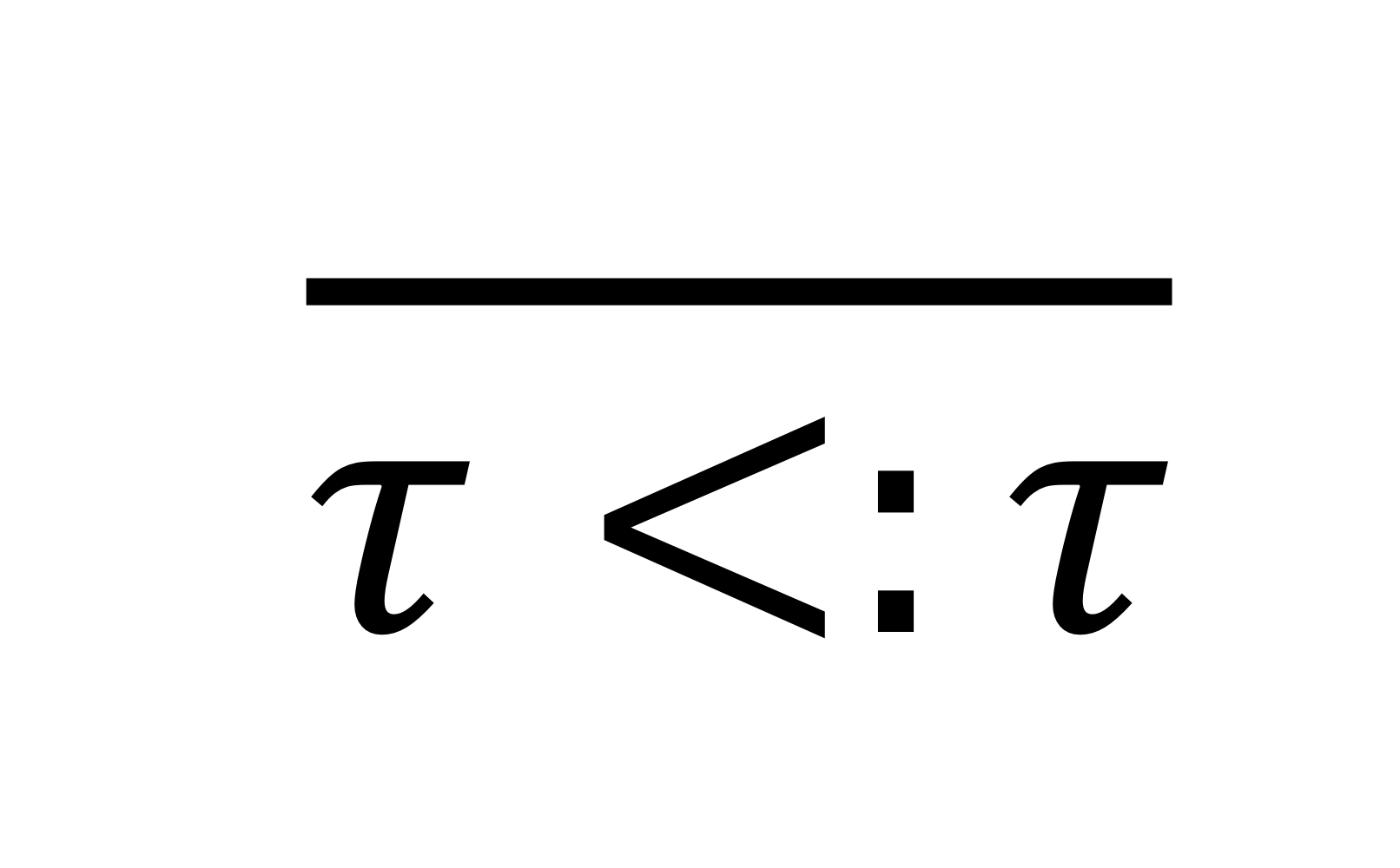
- Transitivity: t1이 t2의 subtype & t2가 t3의 subtype이면 -> t1은 t3의 subtype

- Depth: tuple의 길이가 동일할 때, 내부 scalar가 모두 subtype 관계를 가져야, tuple의 subtype 관계가 성립
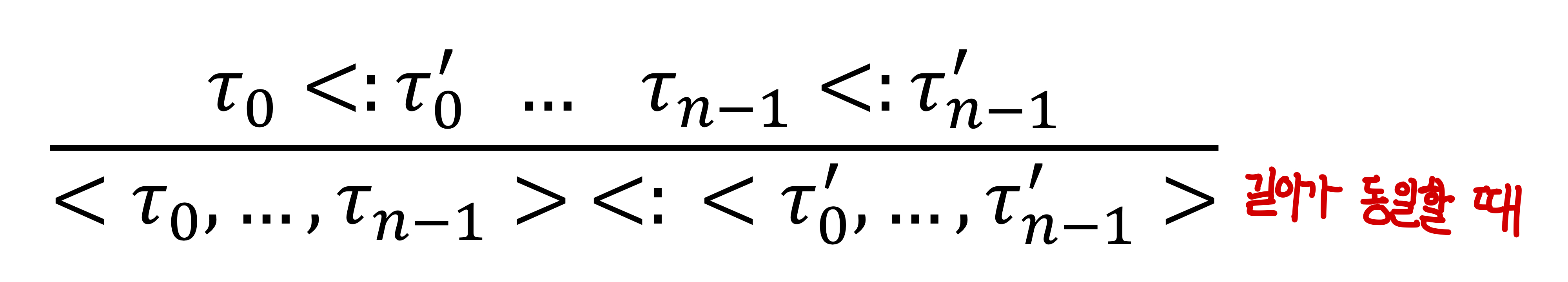
- Width: tuple의 일정 길이를 자른 tuple을 T2, 전체 tuple을 T1이라 할 때, T1은 T2의 subtype

- 추가적으로, int와 <int>는 다른 타입, subtype 관계도 가지지 않음
- Function: argument는 일반화, return은 구체화돼야 subtype이 될 수 있음
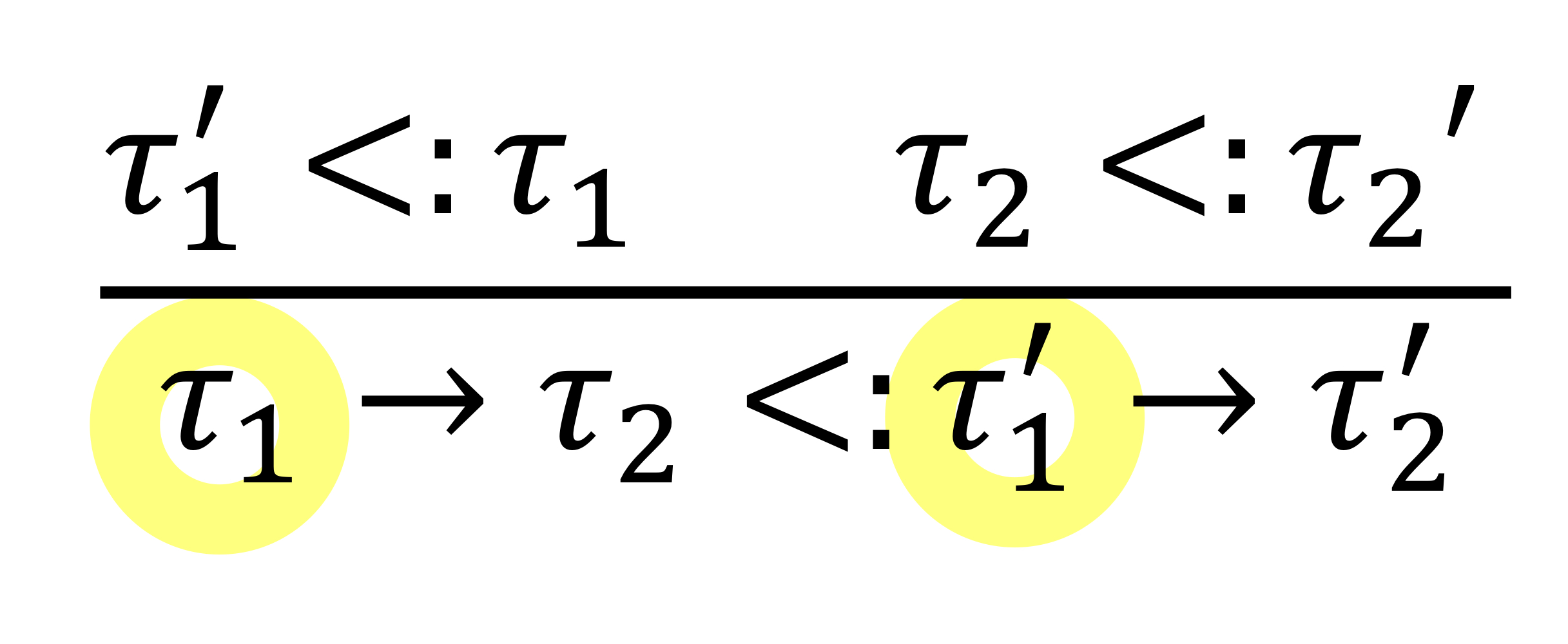

-> 기존에 f를 사용하던 자리에서는 int를 2개만 받아도 됐음,
-> g로 교체되면 input이 2개만 들어오면 문제가 발생
-> g는 f의 subtype이 될 수 없음
- return 또한 마찬가지
-> 기존 f를 사용하던 자리에서는 2개의 return이 필요
-> g로 교체되면 return이 1개만 발생
-> 2개가 필요한 경우 문제 발생

4.2. Subtyping - Join
- Motivation: 다음 expression의 return type?
- if a > 0 then <<3,4>, 5> else <<6>, 7, 8>
- -> if, then, else의 type이 각각 다름
- Join: find least common supertype
- 짧은 쪽 tuple에 맞춤
- join <int> & int -> int?: impossible

-> 짧은 쪽으로 맞추기!!
-> subtype에 가까운 방향
4.3. Subtyping - Meet
- Meet: find most common subtype
- supertype에 가까운 방향
- 함수의 subtype 구할 때,
- argument type: supertype -> meet
- return type: subtype -> join
- ( 이 부분 개념 질문 후에 수정 예정.. )
5. Static Typing vs Dynamic Typing
- Statically Typed Language
- 컴파일 과정에서 all or almost type checking이 완료되는 언어
- 컴파일 단계에서 많은 programming errors 검출
- runtime type checking overheads를 피함
- ex) C, Java, Fun
- 컴파일 과정에서 all or almost type checking이 완료되는 언어
- Dynamically Typed Language
- Almost all type checking이 프로그램 실행 단계에서 완료되는 언어 -> 실행하면서 타입 유추
- static type systems are restrictive
- rapid prototyping is difficult within a static type system
- ex) PHP, Scheme, Python
- Almost all type checking이 프로그램 실행 단계에서 완료되는 언어 -> 실행하면서 타입 유추
- Untyped Language
- No type checking
- ex) Machine codes -> binary 형태이기에 checking 필요 X
- in practice, 정적 Language에도 escape mechanism 존재
- Unsafe casts in C, Java
728x90
반응형
'4학년 1학기 전공 > 컴파일러' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [컴파일러] Chapter 6. Activation Records (0) | 2025.04.23 |
|---|---|
| [컴파일러] Chapter 3. Syntax Analysis(Part 2) (0) | 2025.04.14 |
| [컴파일러] Chapter 3. Syntax Analysis(Part 1) (0) | 2025.04.12 |
| [컴파일러] Assignment 1. Lexical Analysis (0) | 2025.04.12 |
| [컴파일러] Assignment 0. Your First Functional Programming (1) | 2025.03.21 |




