| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
Tags
- LG
- gpt
- 해커톤
- 티스토리챌린지
- 지도학습
- Machine Learning
- ChatGPT
- GPT-4
- LG Aimers
- 딥러닝
- 머신러닝
- 오블완
- supervised learning
- 회귀
- regression
- LG Aimers 4th
- LLM
- deep learning
- Classification
- AI
- PCA
- OpenAI
- 분류
Archives
- Today
- Total
SYDev
[자료구조] Chapter 3. Stack 본문
경희대학교 박제만 교수님의 자료구조 수업을 기반으로 정리한 글입니다.
What is Stack?
- Stack: 가장 마지막에 들어간 데이터가 가장 먼저 나오는 후입선출, LIFO(Last-In, First-Out)의 자료구조를 가진다.
- Logical (or ADT) level:
- stack은 homogeneous items의 집합이다.
- Pop & Push-> stack의 top에서만 발생
1. Stack 자료구조의 ADT
Constructor:
StackType();
- stack의 생성자
Transformer:
void push(ItemType value);
- stack의 top + 1 index에 value 추가
- top++
ItemType pop();
- stack의 top index에 위치한 값을 반환
- top--;
Observer:
int size() const;
- top + 1 반환
bool isFull() const;
- top이 MAX_SIZE - 1과 같다면 true, 그렇지 않다면 false 반환
bool isEmpty() const;
- top이 -1과 같다면 true, 그렇지 않다면 false 반환
2. Stack 자료구조 Implementation
파일명: stack.hpp
#ifndef stack_hpp
#define stack_hpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#define MAX_SIZE 10
using namespace std;
template<class ItemType>
class StackType {
private:
ItemType data[MAX_SIZE];
int top;
public:
StackType();
void push(ItemType value);
ItemType pop();
int size() const;
bool isFull() const;
bool isEmpty() const;
};
template<class ItemType>
StackType<ItemType>::StackType() {
top = -1;
}
// O(1)
template<class ItemType>
void StackType<ItemType>::push(ItemType value) {
if(isFull()) {
cout << "[Error] Stack is Full" << endl;
return;
}
data[++top] = value;
}
// O(1)
template<class ItemType>
ItemType StackType<ItemType>::pop() {
if(isEmpty()) {
cout << "[Error] Stack is Empty" << endl;
return -1;
}
return data[top--];
}
// O(1)
template<class ItemType>
int StackType<ItemType>::size() const {
return (top + 1);
}
// O(1)
template<class ItemType>
bool StackType<ItemType>::isFull() const {
return (top == MAX_SIZE - 1);
}
// O(1)
template<class ItemType>
bool StackType<ItemType>::isEmpty() const {
return (top == -1);
}
#endif /* stack_hpp */
파일명: main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "stack.hpp"
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
int item = 7;
StackType<int> tempStack;
tempStack.push(item);
tempStack.push(3);
tempStack.push(6);
tempStack.pop();
tempStack.push(4);
while(!tempStack.isEmpty()) {
item = tempStack.pop();
}
return 0;
}
Class Template
- class type의 multiple versions를 만들 수 있게함 -> type parameters 이용
- template definition에 formal(형식적인) parameter 등장, client code에 actual parameter 등장 -> 모두 <>에 둘러싸임
- built-in or user-defined(struct or class) 모두 사용 가능
- .h와 .cpp로 나눠서 사용하면 안 됨
>> Class Template allow you to have data type-independent and flexible codes.
Null Pointer (nullptr)
- Null pointer는 0의 상수 -> #define NULL 0
- 그러나 function overloading 상황에서, compiler가 받아들이기에 ambiguous(모호)하다.

-> NULL parameter로 함수를 호출하면 func(int)를 호출
-> nullptr parameter로 함수를 호출하면 func(char *)를 호출
Memory Allocation
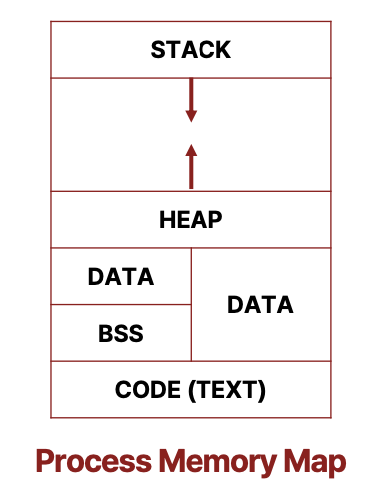

- stack: 지역변수 - 함수 내부의 변수들
- heap: 동적 할당을 위한 공간
- data: 전역 변수 - 초기화/초기화되지 않은 변수들
- code: 프로그램의 코드
| Variable Type | Allocation Time | Deallocation | Allocation Type | Location | Size Change |
| Local Variable | Function call | Function termination |
Automatic allocation |
STACK segment |
Fixed |
| Variables with dynamic sizes |
Instructions New, malloc() |
Instructions delete, free() |
Dynamic allocation |
HEAP segment |
Flexible |
| Static/global Variables |
Compile time (Program starts) |
Program termination |
Static allocation |
Data segment | Fixed |
- Automatic Allocation

- Dynamic Allocation
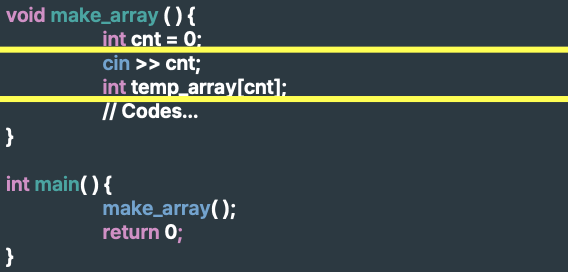
-> local variable의 크기는 compile 시점에 이미 결정되어 있어야 한다.
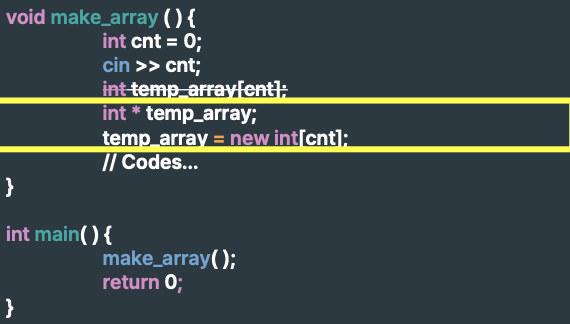
-> 동적 할당하는 경우에는 사이즈를 미리 정하지 않아도 괜찮음

-> 동적으로 메모리를 할당하는 경우, 반드시 explicitly(명시적으로) 할당을 해제해야 한다.
-> delete (or free)

How to prevent garbage?
- 할당된 공간을 delete
- pointer를 유지
- Static Allocation
- DATA segment의 size는 compilation 이후 변경 불가
- too many global/static variables -> prgoram will become too large
728x90
반응형
'3학년 2학기 전공 > 자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [자료구조] Chapter 5. Linked Structures (0) | 2024.10.14 |
|---|---|
| [자료구조] Chapter 4-1. Programming Tips (2) | 2024.10.02 |
| [자료구조] Chapter 4. Queue (0) | 2024.09.30 |
| [자료구조] Chapter 2. Unsorted/Sorted Lists (0) | 2024.09.17 |
| [자료구조] Chapter 1. Software, Data Structure, and C++ (0) | 2024.09.13 |




