| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
Tags
- regression
- LG Aimers 4th
- OpenAI
- LG
- 지도학습
- 티스토리챌린지
- Machine Learning
- 머신러닝
- 분류
- AI
- 딥러닝
- supervised learning
- LLM
- 오블완
- 해커톤
- PCA
- GPT-4
- gpt
- deep learning
- Classification
- ChatGPT
- LG Aimers
- 회귀
Archives
- Today
- Total
SYDev
[자료구조] Chapter 4-1. Programming Tips 본문
경희대학교 박제만 교수님의 자료구조 수업을 기반으로 정리한 글입니다.
Call by X
1. Swap Example 1

- swap1_a = 3, swap1_b = 5
- call by value
- Looking into 'Swap1'
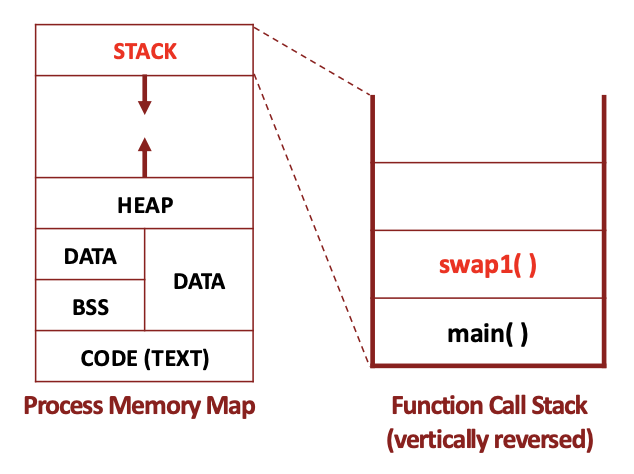

2. Swap Example 2

- swap2_a = 5, swap2_b = 3
- call by reference
3. Swap Example 3

- swap3_a = 5, swap3_b = 3
- call by address
4. Swap Example 4

- swap4_a = 3, swap4_b = 5
- 주소값 자체는 복사된 값이기 때문에, 주소를 교체하고 싶으면 주소의 주소를 가리키는 double ptr를 사용하면 될 듯?
5. Improved Swap Example 4
- 그렇다면 double ptr를 사용하면 원래 의도대로, ptr이 가리키는 주소를 바꾸는 방식을 사용할 수 있을까?
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void swap4(int ** a, int ** b) {
int * temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
return;
}
int main() {
int swap4_a = 3;
int swap4_b = 5;
int * p4_a = &swap4_a;
int * p4_b = &swap4_b;
cout << &swap4_a << "/" << &swap4_b << endl;
swap4(&p4_a, &p4_b);
cout << &swap4_a << "/" << &swap4_b << endl;
}
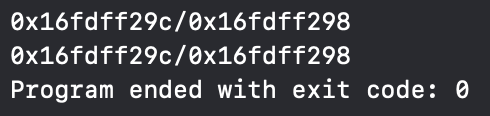
-> 바뀌지 않는다!
1. p4_a는 swap4_a의 주소를 가리키고 있고, p4_b는 swap4_b의 주소를 가리킴
2. swap4(&p4_a, &p4_b)를 호출하면 p4_a와 p4_b가 가리키는 주소가 서로 바뀜
3. 하지만 swap4_a와 swap4_b라는 변수 자체의 메모리 주소는 그대로 유지 -> 이는 main 함수에서 선언된 변수이기 때문(main 함수가 실행되는 동안 메모리 주소 고정)
해결책
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void swapPointers(int** a, int** b) {
int* temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
int main() {
int* swap4_a = new int(3); // 동적 할당
int* swap4_b = new int(5); // 동적 할당
cout << "Before swap:" << endl;
cout << "Address of swap4_a: " << swap4_a << ", Address of swap4_b: " << swap4_b << endl;
cout << "Value of *swap4_a: " << *swap4_a << ", Value of *swap4_b: " << *swap4_b << endl;
// Swap the pointers
swapPointers(&swap4_a, &swap4_b);
cout << "After swap:" << endl;
cout << "Address of swap4_a: " << swap4_a << ", Address of swap4_b: " << swap4_b << endl;
cout << "Value of *swap4_a: " << *swap4_a << ", Value of *swap4_b: " << *swap4_b << endl;
// 동적 할당 해제
delete swap4_a;
delete swap4_b;
return 0;
}
1. swap4_a와 swap4_b는 동적으로 메모리를 할당받고, 각각 다른 메모리 주소에 저장
2. swapPointers 함수를 사용하여 이 포인터들이 가리키는 주소를 서로 바꿈
3. 결과적으로, 포인터가 가리키는 주소가 바뀌었기 때문에 출력된 주소 값도 서로 바뀜
이런 방식이 가능한 이유?
-> c라는 언어의 자유도 때문으로 추정
>> 주소를 바꾸는 시도 자체가 굉장히 위험한 시도이기 때문에, 아마 최근 release되는 memory access가 굉장히 엄격한 언어에서는 불가능할 것이다!! (하지 않는 것을 추천)
When We Use 'Return by Reference?
- return object의 크기가 너무 클 때
- multiple objects/variables를 반환하고 싶을 때
- 동적으로 할당된 objects를 반환하고 싶을 때
Inheritance
- 기존에 존재하던 class에 특화된 새로운 class를 만들 수 있게함
- new classs is called a derived class(child class) of the existing class
- existing class is called base class(parent class) of the new class
- CountedQueue Constructor
template<class itemType>
class CountedQueueType: public QueueType<ItemType> {
private:
int length;
public:
CountedQueueType();
...
}template<class ItemType>
CountedQueueType<ItemType>:CountedQueueType(int maxQue): QueueType<ItemType>(maxQue) {
length = 0;
}
Overriding vs. Overloading
- Function Overrding
- base class에 정의된 method를 customize or extend하여 derived class에 구현하는 능력
- 같은 이름, parameters(numbers and types), return type을 가짐
- Function Overloading
- same scope에서 이름은 같지만, parameter lists가 다른 multiple functions를 정의하는 능력
- 다른 parameters와 return type을 가질 수 있음
- ex) add(int a, int b); add(float a, float b), add(int a, int b, int c), ...
Polymorphism
- language가 inheritance hierarchy에서 중복된 method names를 가질 수 있으며, method가 적용되는 object에 적합한 method를 적용할 수 있는 언어의 기능
- polymorphism은 function overriding과 function overloading을 모두 포함
728x90
반응형
'3학년 2학기 전공 > 자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [자료구조] Chapter 5. Linked Structures (0) | 2024.10.14 |
|---|---|
| [자료구조] Chapter 4. Queue (0) | 2024.09.30 |
| [자료구조] Chapter 3. Stack (3) | 2024.09.30 |
| [자료구조] Chapter 2. Unsorted/Sorted Lists (0) | 2024.09.17 |
| [자료구조] Chapter 1. Software, Data Structure, and C++ (0) | 2024.09.13 |




