| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 |
| 30 |
- 티스토리챌린지
- LG
- LG Aimers 4th
- PCA
- gpt
- 해커톤
- supervised learning
- regression
- 오블완
- 지도학습
- AI
- ChatGPT
- LG Aimers
- 회귀
- 머신러닝
- LLM
- 딥러닝
- OpenAI
- Classification
- Machine Learning
- 분류
- deep learning
- GPT-4
- Today
- Total
SYDev
[운영체제] Chapter 4. Thread & Concurrency 본문
경희대학교 허선영 교수님의 운영체제 수업을 기반으로 정리한 글입니다.
Thread
1. Thread
- Thread: Basic Unit of CPU Utilization
- program의 execution flow
- multi-thread -> thread가 여러 개 -> 서로 다른 thread는 각각 다른 instructions 수행
- single thread -> data,files,code 하나
- multi thread -> data,files, code 공유 / registers, stack, pc 개별 소유
- different thread -> different code
- 같은 process에서 서로 다른 code를 가리킴
- 실행하는 위치가 다르니 pc도 다름
- registers도 다름
- stack은 function을 호출할 때 생성 -> 그러니 stack도 다름


-> Multi-threaded Program에서 task1와 task2는 simultaneous하게 동작
- Thread 구성요소
- Thread ID
- Program Counter (PC)
- Register Set
- Stack
- Thread가 Process 내에서 공유하는 것들
- Code section
- Data section
- Open files
- Signals
- Others
2. Thread in Memory

-> thread마다 각자의 stack을 가짐
3. Benefits
- Responsiveness
- process의 일부가 blocked 상태 -> execution이 이어지도록 함 -> user interface에서 중요
- Resource Sharing
- threads는 process의 resources를 공유
- shared memory나 message queue를 사용하는 것보다 쉬움
- Economy
- process creation보다 비용이 cheaper
- context switching보다 lower overhead
- Scalability
- process가 multicore architecture의 이점을 얻을 수 있음
->> 대부분의 kernels는 multithreaded
4. Use Cases
- Case 1: Multitheaded Serer Architecture
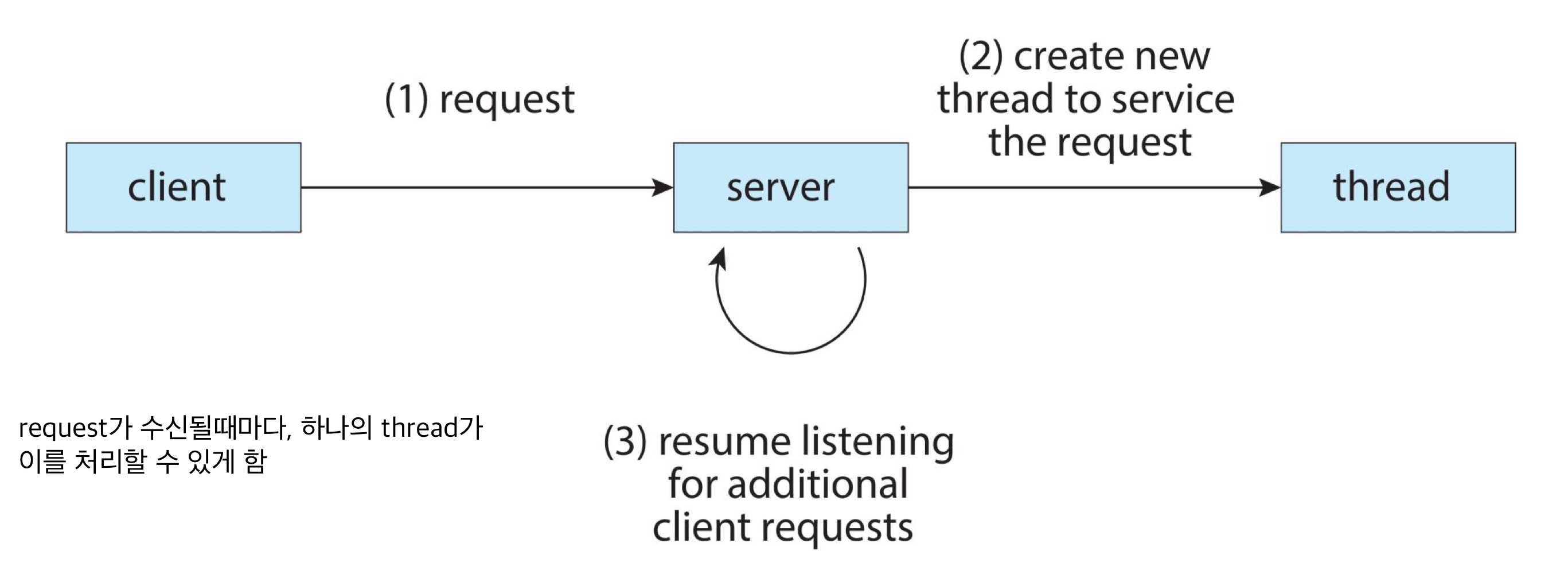
- request를 받아서, 해당 request를 처리하기 위한 새로운 threaed를 생성하고, server는 계속해서 requests를 받는 형태
- Case 2: Loop Parallelization on Multi-core Systems
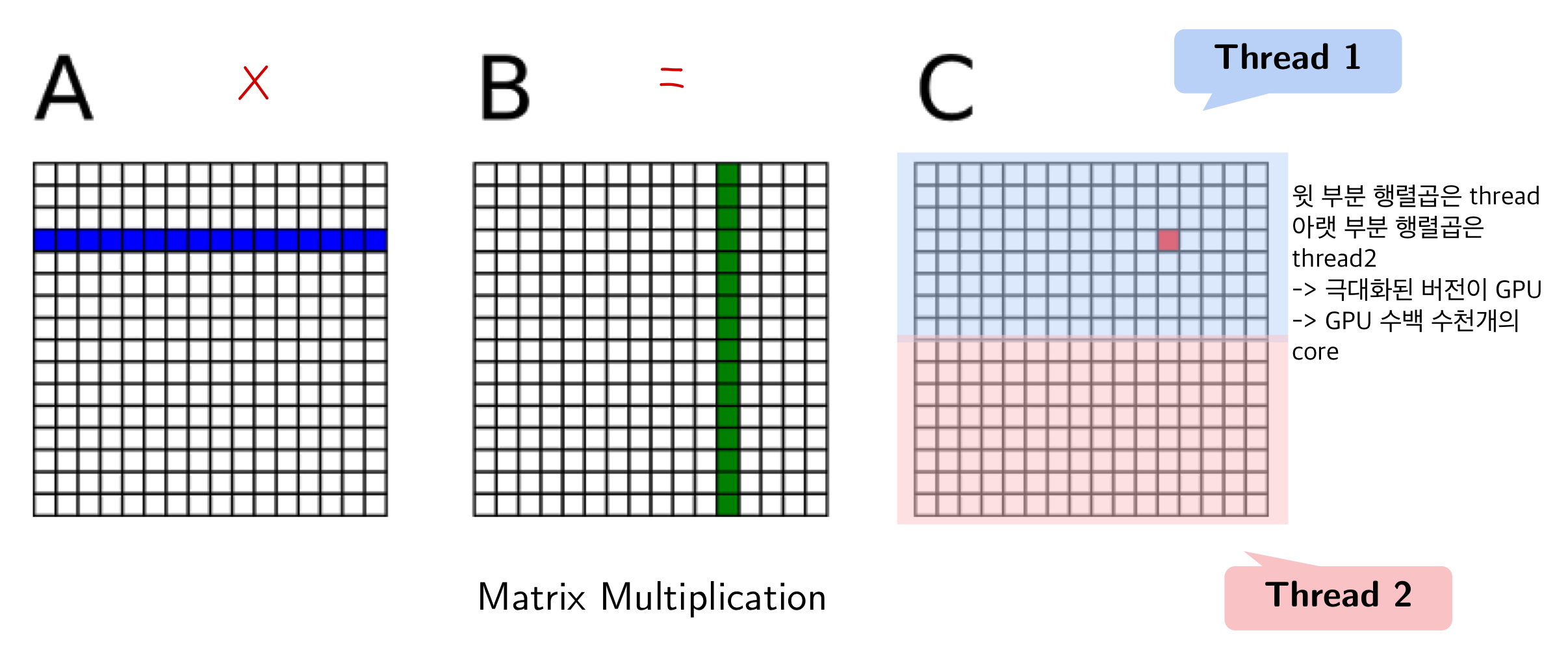
- 행렬곱 계산의 효율의 극대화
Parallelism vs Concurrency
https://sypdevlog.tistory.com/314
[풀스택서비스프로그래밍] parallelism vs concurrency
1. Parallel Computingdef(wikipedia): simultaneously(동시에) 많은 계산을 하는 연산의 한 방법 -> 실제로 한 번에 많은 작업을 처리크고 복잡한 문제를 작게 나눠 동시에 병렬적으로 해결하는 데에 주로 사용
sypdevlog.tistory.com
-> 해당 게시물에서 자세하게 다룬 개념
1. Parallelism
- Parallelism: simultaneously(동시에) 많은 계산을 하는 연산의 한 방법 -> 실제로 한 번에 많은 작업을 처리
- physical하게 동시에 실행
- 한 시점에 여러 개의 thread
- Types of parallelism
- Data parallelism: 같은 operation, but 다른 data subsets(core 간에) -> Distribution of Data
- Task parallelism: Unique operation(core 간에) -> Distribution of Tasks
Data parallelism: 프로그램이 각 data를 parallel하게 처리하는 것 -> 각 data는 동일한 process로 처리
Task parallelism: 프로그램이 각 task를 parallel하게 처리하는 것
- N개의 프로세서가 func1(), func2(), ... , funcN()을 맡아 처리
Pipeline parallelism: 프로그램이 pipeline 구조로 설계되어 data를 병렬로 처리 -> 이때 pipeline의 각 stage는 다른 task 실행
참고자료: https://computing-jhson.tistory.com/12
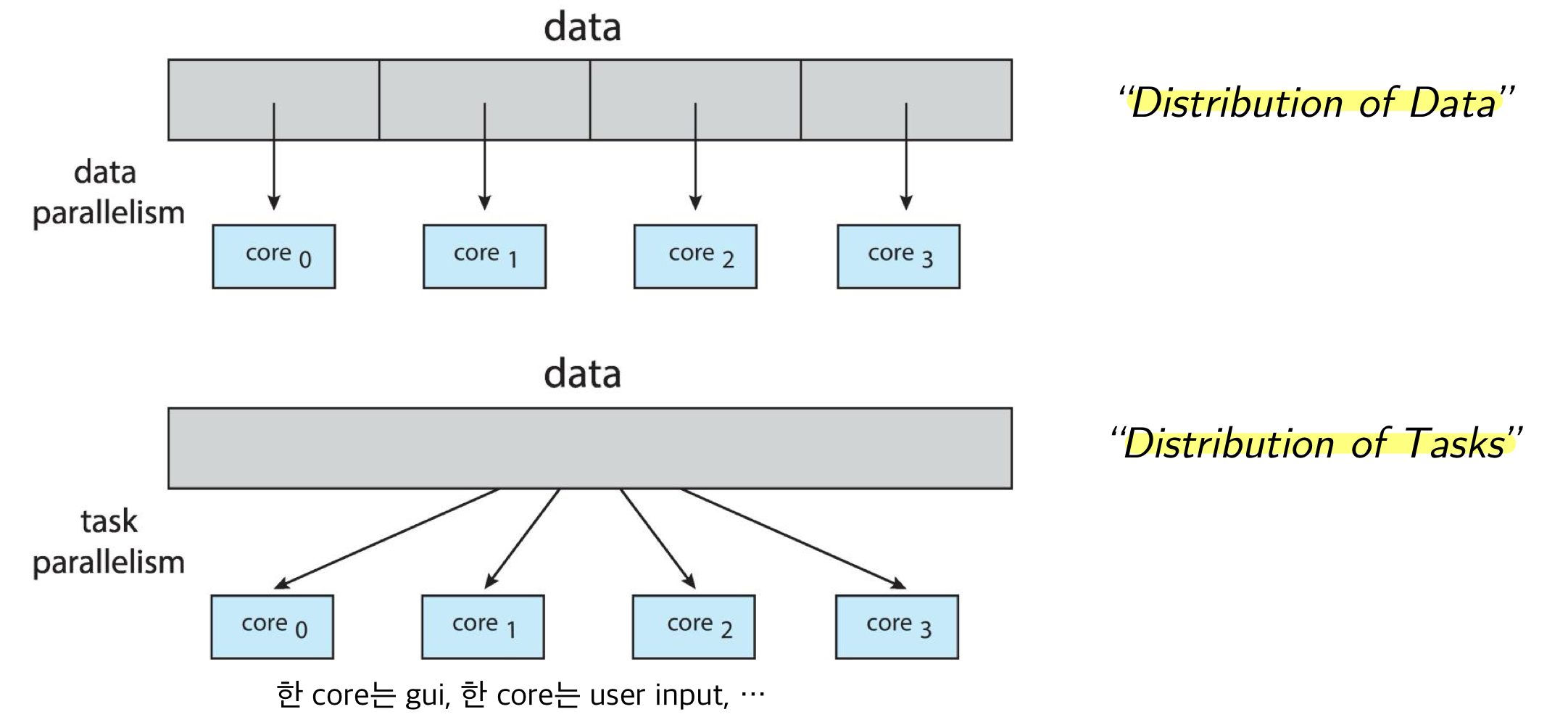
2. Concurrency
- Concurrency: concurrently(병행) 방식으로 연산하는 방법 -> 다른 계산이 모두 끝날 때까지 기다리지 않고, 다른 계산을 진행
- 한 번에 하나의 task
- 여러 개의 thread를 관리하면서 실행, but 한 시점에 하나의 thread
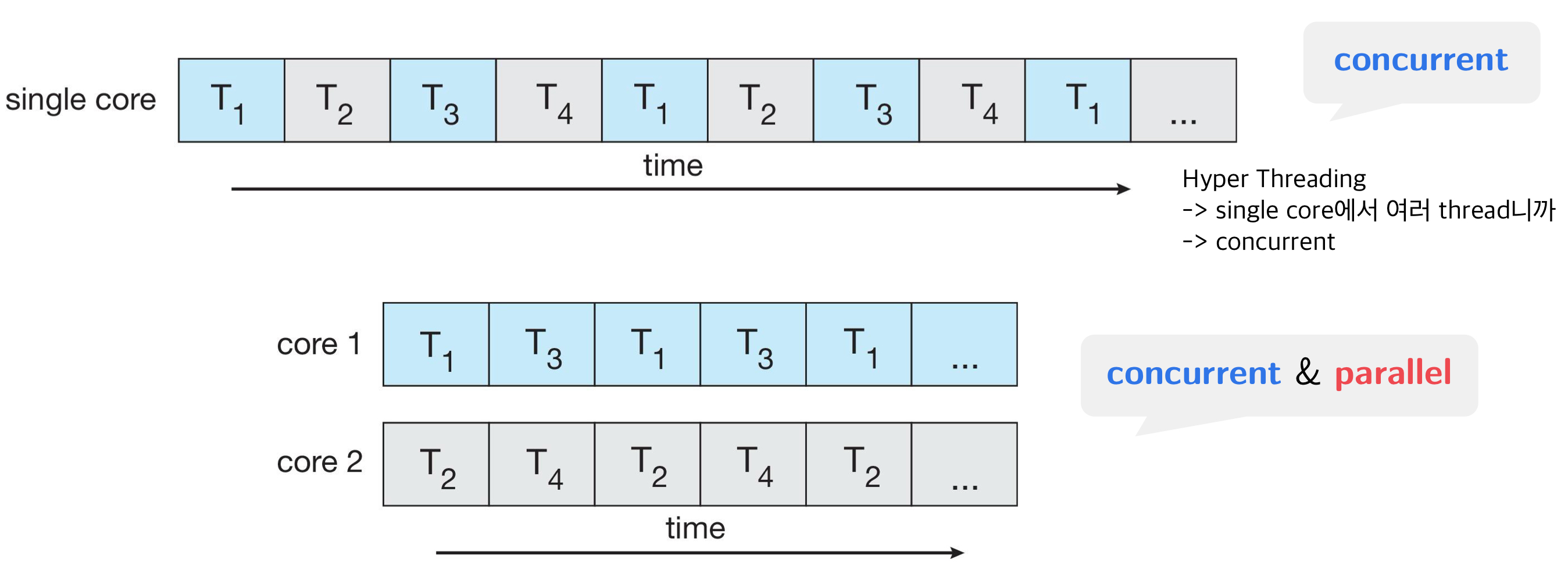
Multicore Processing
1. Background
- Single threaded CPU의 performance가 더이상 빠르게 증가하지 않음

-> 무어의 법칙이 깨졌다!!
2. Multicore Programming
- Multicore or Multiprocessor systems -> 프로그래머가 직접 구현해야 함
- Challenges
- Identifying tasks -> 각각의 core가 어떤 작업을 해야하는지 설정
- Balance -> Load balancing
- Data splitting
- Data dependency
- Testing and debugging
- ->>> 모두 programmer의 몫
- Thread Libraries for programmers
- POSIX Pthreads(pthreads)
- programming language와 독립적으로 존재하는 (parallel) execution model
- pthread -> IEEE Standard와 Institue of Electrical에 의해 정의된 API
- 참고자료: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pthreads
- Windows threads
- Java threads
- POSIX Pthreads(pthreads)
3. Amdahl's Law
- serial and parallel components를 모두 가진 application에 additional cores를 추가했을 때, 향상되는 performance의 지표

-> Parallel portion 항이 존재할 때, core의 수 N이 커지면 Speedup이 커짐
- ex) 75% parallel, 25% serial일 때, 2개의 core -> s=0.25, p=0.75 -> 1/( 0.25 + 0.75/2 ) ~= 1.6 -> 1.6배 속도 향상
- N이 무한으로 갈 때, -> speedup은 1/S에 근접한다.
- serial portion은 additional core를 추가할 때, application에 불균형한 영향을 미친다. -> 아무리 많은 수의 core를 추가해도, serial portion이 남아 있다면, 전체 서능 향상은 제한적일 수 있다.

-> core가 2가 되면, P 영역이 반으로 줄어듦

-> core 개수가 많아질수록, multi-thread로 구현하지 않으면 성능 차이가 크다.
User and Kernel Threads
- User threads -> user-level threads library에 의해 관리됨
- Kernel threads -> kernel의 보조를 받음
- user/kernel threads 사이에 관계는 반드시 존재
- Multithreading models -> mapping 방식에 따라 3가지 model로 나뉨
- Many-to-One
- One-to-One
- Many-to-Many
1. Many-to-One
- Many user-level threads -> mapped to single kernel thread
- kernel thread가 1개 -> 한 번에 오직 한 개의 thread만 kernel에 접근 가능
- 하나의 thread가 I/O request를 실행해야 함 -> 다른 모든 process는 blocked
- Multiple threads가 multicore system에서 parallel하게 작동하지 않음 -> concurrency는 가능, parallelism 불가능
- examples
- Solaris Green Threads
- GNU Portable Threads

2. One-to-One
- Each user-level thread -> maps to kernel thread
- user-level thread 생성 -> kernel thread 생성
- many-to-one보다 concurrency 활용성이 좋음
- large number of threads -> system의 performance에 부담을 가함
- overhead에 의해서 process 당 threads가 제한될 수 있음
- examples
- Windows
- Linux
- 가장 일반적으로 사용하는 방식

3. Many-to-Many Model
- Many user level threads -> mapped to many kernel threads
- os가 충분한 수의 kernel threads를 생성할 수 있음
- Windows with the ThreadFiber package
- 일반적이지는 않음 -> 구현이 어려움

Thread Libraries
- Thread library: threads를 만들고 관리하는 API를 programmer에게 제공
- Two primary ways of implementing
- Library entirely in user space
- Kernel-level library supported by the OS
1. Pthreads
- POSIX standard API for creation and synchronization
- POSIX standard -> thread는 이렇게 만들어라, systemcall은 이렇게 호출해라, 이렇게 관리해라, .. 하는 규정
- user-level 혹은 kernel-level로 제공
- Specification(명세), not Impelmentaion -> 구현된 거 가져다 쓰기만 하면 됨
- API는 thread library의 동작을 명세한다.
- Implementaion은 library의 구현에 달려있다.
- UNIX os에서 일반적
- Taks -> function으로 정의
void* task (void *arg);- Thread Creation <-> fork()
int pthread_create(pthread_t *restrict thread,
const pthread_attr_t *restrict attr,
void *(*start_routine)(void *),
void *restrict arg);
- Thread Join <-> wait()
int pthread_join(pthread_t thread, void **retval);
- Thread Termination
noreturn void pthread_exit(void *retval);
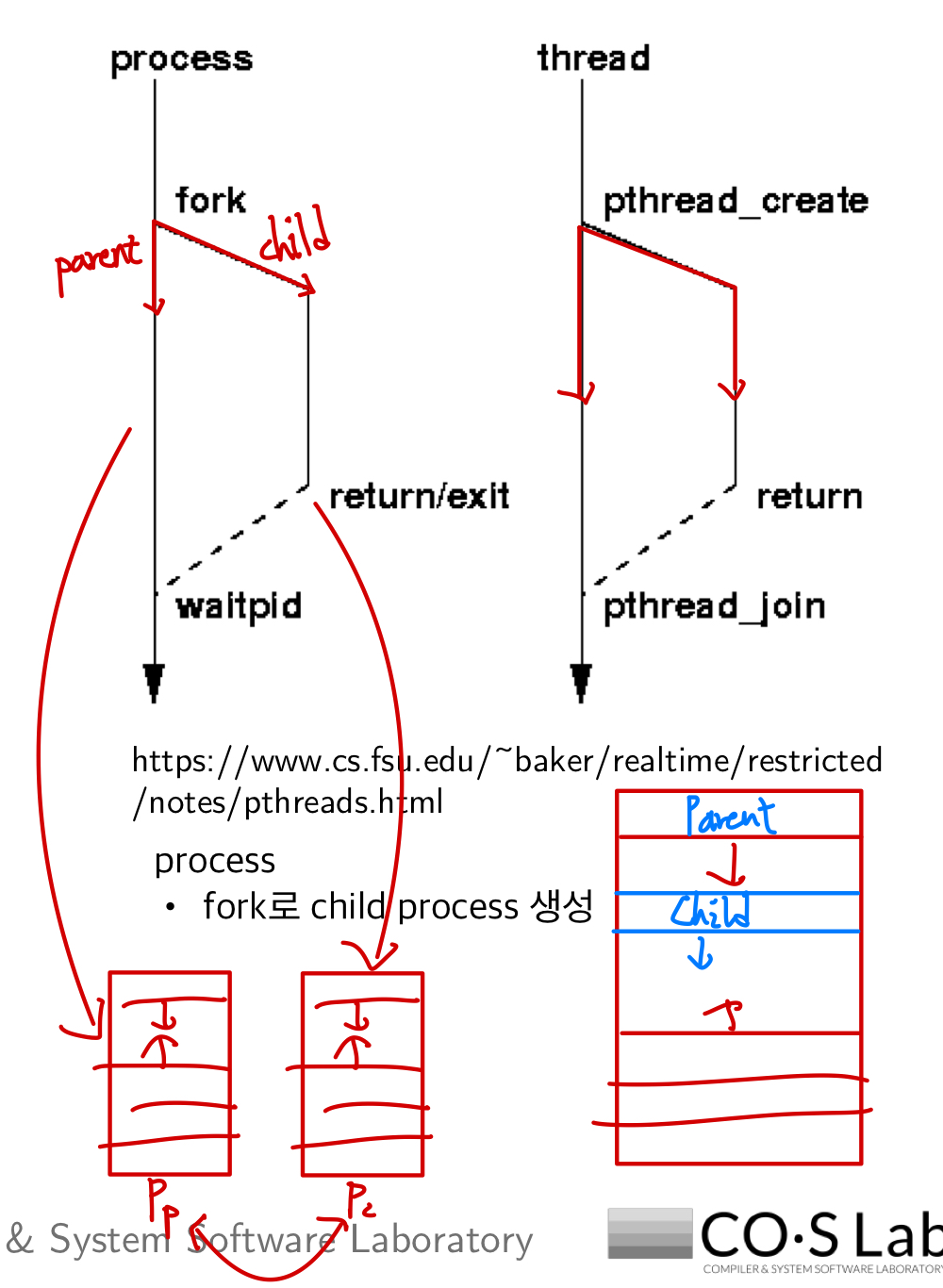
2. Pthreads Example

- main 함수에서 main thread 시작
- pthread_create -> child threaed(runner) 생성
- runner는 따로 실행
- main thread는 pthread_join 시점에서 child thread(runner)가 종료(pthread_exit)되기까지 대기
- 해당 예시에서는 main thread가 대기만 하므로, performance 이득 X
3. Thread Cancellation
- thread가 완료되기 전에, Terminating해야 함
- Asynchronous cancellation: target thread를 즉시(immediately) 종료
- Deferred cancellation: target thread가 cancel되어야 하는지 주기적으로 체크 -> cancel 가능 상황에서 종료 -> 안전한 상황에서만 종료되도록 연기하는 것

- thread cancellation 호출은 cancellation을 요청 -> but, thread의 실질적인 cancellation은 thread state에 달려 있음
| Mode | State | Type |
| Off | Disabled | - |
| Deferred | Enabled | Deferred |
| Asynchronous | Enabled | Asynchronous |
- thread가 cancellation disabled일 때, enable 사앹가 되기 전까지 pending 상태를 유지
- Default type - deferred
- Cancellation은 cancellation point에 도달했을 때만 발생
- pthread_testcancel() -> 내가 cancel하고 싶은 지점을 명시
- 이후 cleanup handler가 호출됨
- cleanup handler? -> thread의 termination을 위해 필요한 것을 user가 탐색하는 special한 과정을 포함하는 routines(user에 의해 작성됨)
- 참고자료: https://www.ibm.com/docs/en/zos/2.4.0?topic=requirements-cleanup-threads
참고자료
Thread (computing) - Wikipedia
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Smallest sequence of programmed instructions that can be managed independently by a scheduler A process with two threads of execution, running on one processor Program vs. Process vs. Thread Scheduling, Preemption, Con
en.wikipedia.org
pthreads - Wikipedia
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Execution model which allows for parallel computing In computing, POSIX Threads, commonly known as pthreads, is an execution model that exists independently from a programming language, as well as a parallel execution
en.wikipedia.org
pthreads.html
POSIX Threads API Overview The POSIX threads API is designed to allow maximum freedom to implementors This means the API is not "robust" against mis-use This means the semantics of several operations are only very loosly defined, and so may have quite diff
www.cs.fsu.edu
'3학년 2학기 전공 > 운영체제' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [운영체제] Exercise 2. Process Management (0) | 2024.10.10 |
|---|---|
| [운영체제] Chapter 5. CPU Scheduling (5) | 2024.10.09 |
| [운영체제] Chapter 3. Processes (4) | 2024.09.24 |
| [운영체제] Exercise 1 (1) | 2024.09.14 |
| [운영체제] Chapter 2. Operating System Structures (2) | 2024.09.10 |




